Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-021
Contemporary Management of Diabetic Calcific Diffusely Diseased Female Coronaries-A Combination of Coronary Imaging and Intravascular Lithotripsy
By Debdatta Bhattacharyya, Ayan Kar, Pankaj Singh
Presenter
Ayan Kar
Authors
Debdatta Bhattacharyya1, Ayan Kar2, Pankaj Singh2
Affiliation
RN Tagore Hospital, India1, NH-Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, India2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-021
Coronary - Adjunctive Procedures (Thrombectomy, Atherectomy, Special Balloons)
Contemporary Management of Diabetic Calcific Diffusely Diseased Female Coronaries-A Combination of Coronary Imaging and Intravascular Lithotripsy
Debdatta Bhattacharyya1, Ayan Kar2, Pankaj Singh2
RN Tagore Hospital, India1, NH-Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, India2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
62-year diabetic hypertensive presented with unstable angina for 3 months despite best-tolerated guideline-directed medical therapy. She underwent a CAG which showed calcific TVD. She had severe LV systolic dysfunction with an LVEF of 30%. After the institutional Heart team meeting, she was advised PTCA to the LAD in view of diffuse disease in the distal target vessels .
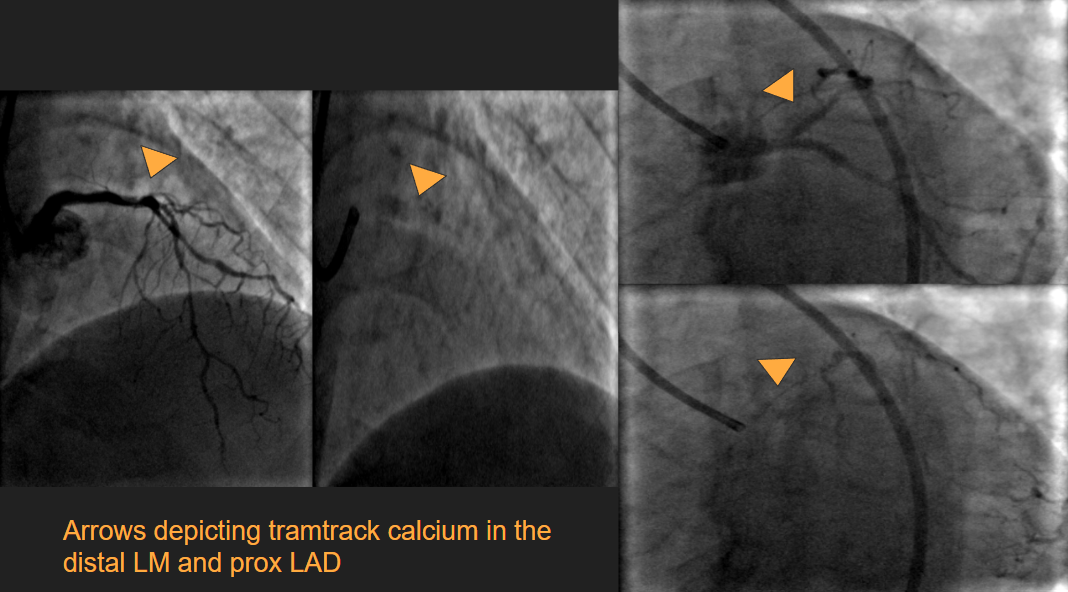




Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Hemoglobin 12.3g/dlcreatinine: 1.25 mg/dl ECG : Evolved anterior wall MI ECho: RWMA in LAD territory with an LVEF 30%

Relevant Catheterization Findings
Left Main: the body of the Left main and shaft show adventitial calciumLAD shows ostioproximal 4o to 50% tubular disease with long segment adventitial calcium, followed by two tandem lesions each measuring 80-90 % in the mid-LAD. The distal LAD is also also diffusely diseased.LCX: Non-dominant with 50 to 60 % disease in the mid-part and 70 to 80 % disease in the mid-distal junction RCA: dominant and has diffuse 50 to 60% disease in the mid part.The distal PDA and PLV also have minor plaques
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
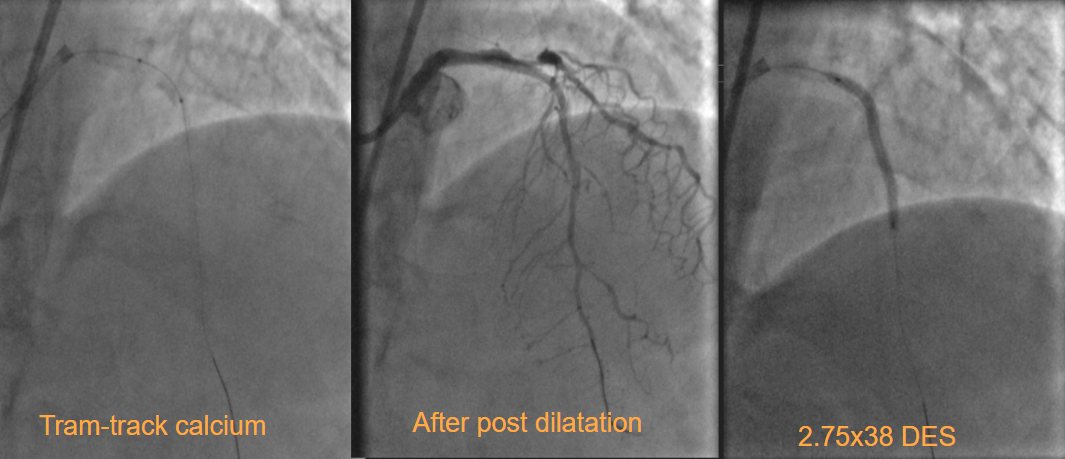
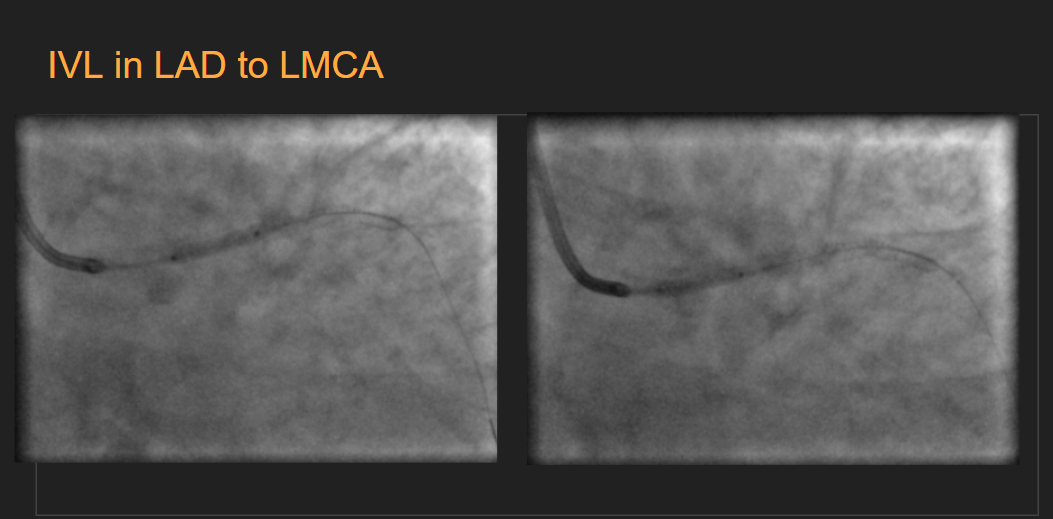
The Left Main was engaged with a 7F SPB 3.0 catheter and the LAD was wired with a 0.014 Asahi Sion Blue wire. After wiring IVUS interrogation to the LAD showed long segments of calcific disease involving the entire extent of the ostioproximal and Mid LAD with the prox mid junction reporting almost a close to 270-degree arc of calcium and fibro calcific plaques involving the ostio-proximal LAD. A suitable landing zone with less than 50% plaque burden was chosen in the mid-LAD with a distal diameter close to 3.0 on IVUS . Predilatation to the LAD was done with a 2.5x 15 at 18atm.The mid distal LAD was stented with a 2.75x38DES deployed at 10ATM and post-dilated with a 3x15 NC balloon at 16atm proximally. Repeated attempts to dilate the proximal LAD with the 3.0x15 Nc balloon resulted in residual waists which were persistent. IVL 3x12 was deployed and 8 cycles of 10 pulses each were deployed to the distal lMCA and Ostial LAD . Post IVL the LAD was pre-dilated with a 3.5x 12 NC balloon at 18atm with no residual dog boning noted. The proximal lAD to distal LMCA was stented with a 3.5 x 28 DES post-dilated with a 4.0 x 8 mm DES at 16 atm. Final IVUS run showed good stent expansion, no evidence of mal-apposition/edge dissection, and significant luminal gain .




Case Summary
Diabetic female coronaries are notorious for long-segment calcific diffuse disease often resulting in poor sizing and underexpanded stents. Judicious use of intravascular imaging and plaque modification devices like Intravscular lithotripsy help in better lesion preparation and optimal stent deployment and immaculate stent apposition and is likely to reduce overall target lesion failure rates in this critical subpopulation which is often widely considered a poor subset for coronary angioplasty.

