Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-177
Optical Coherence Tomography Guided Bifurcation Percutaneous Coronary Intervention and Optical Coherence Tomography - Based Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis
By Chi-Ting Lu, Wei Chieh Huang, Tse-Min Lu
Presenter
Chi-Ting Lu
Authors
Chi-Ting Lu1, Wei Chieh Huang2, Tse-Min Lu2
Affiliation
Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taoyuan Branch, Taiwan1, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-177
Coronary - Imaging & Physiology - Invasive Imaging (IVUS, OCT, NIRS, VH, etc)
Optical Coherence Tomography Guided Bifurcation Percutaneous Coronary Intervention and Optical Coherence Tomography - Based Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis
Chi-Ting Lu1, Wei Chieh Huang2, Tse-Min Lu2
Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taoyuan Branch, Taiwan1, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 73-year-old male has a history of hypertension. He was an ex-smoker with heavy smoking for two packs per day for 20 years. In recent six months, he developed intermittent chest tightness and exertional dyspnea. The symptoms could be exacerbated with heavy exercise, and partially relieved after rest. On admission, his vital signs were as follows: temperature of 37°C, pulse rate of 68 bpm, respiratory rate of 17 /min, blood pressure of 165 / 79 mmHg, and oxygen saturation of 96% on room air.


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Laboratory studies on admission demonstrated a normal blood cell count, normal cardiac enzymes level, normal liver and renal function. Electrocardiography displayed sinus rhythm with first degree atrioventricular block. Chest radiography showed cardiomegaly and prominence of pulmonary vascularity in bilateral hilar region. The patient underwent elective coronary angiography (CAG) as schedule.
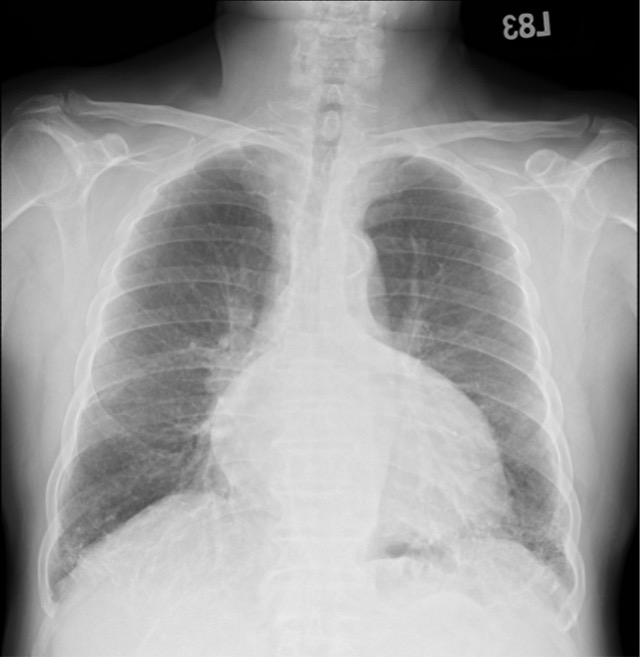

Relevant Catheterization Findings
The CAG performed via right radial artery revealed heavily calcified left main (LM) coronary bifurcation (Medina binary classification 1,1,1) and triple vessel disease (TVD) with proximal left anterior descending (LAD) coronary lesion (diameter stenosis about 70%), diffuse long left circumflex (LCx) coronary lesion (diameter stenosis about 80%), and proximal to distal diffuse long right coronary (RCA) lesion (diameter stenosis about 80%).
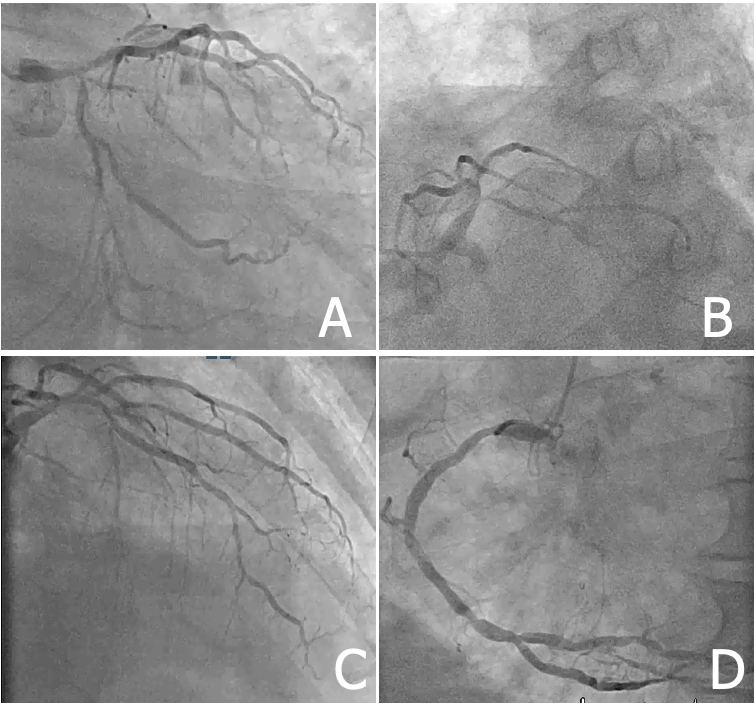

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
We engaged LMCA with a 7 Fr SL 3.5 guide catheter; a Sion Blue guide wire (GW) and a Sion GW were advanced to LAD-D and LCx-D. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) from LAD to LM showed severe circumferential calcification; OCT-based calcium score was 4. OCT from LCx to LM showed fibro-lipidic and fibro-calcified plaque; OCT-based calcium score was 1. Six runs of rotational atherectomy (RA) were performed using a 2.0 mm Rota burr with a Rota extra-support GW, with rotational speed of 126 k to 151 k rpm. Post-RA OCT showed increased luminal area and decreased minimal calcium thickness at LM bifurcation and LAD-P. 3D reconstructed OCT image implied low possibility of compromised side branch, we decided provisional LM to LAD stenting, followed by proximal optimization technique (POT), rewiring for stent struct opening of LCx ostium, kissing dilation, and final POT of LM. Post-stenting OCT showed good stent expansion and apposition. Angiogram showed good results with TIMI III blood flow in both LAD and LCx. We reconstructed the OCT images of target vessel before and after PCI to process the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis offline. The circumferential time-averaged wall shear stress (WSS) and calcium volumetry were evaluated. The velocity and WSS of LM bifurcation and proximal LAD level were significantly improved after RA and after optimized stenting, which implied a good result of intervention. The patient reported no adverse effect at three years of follow-up.
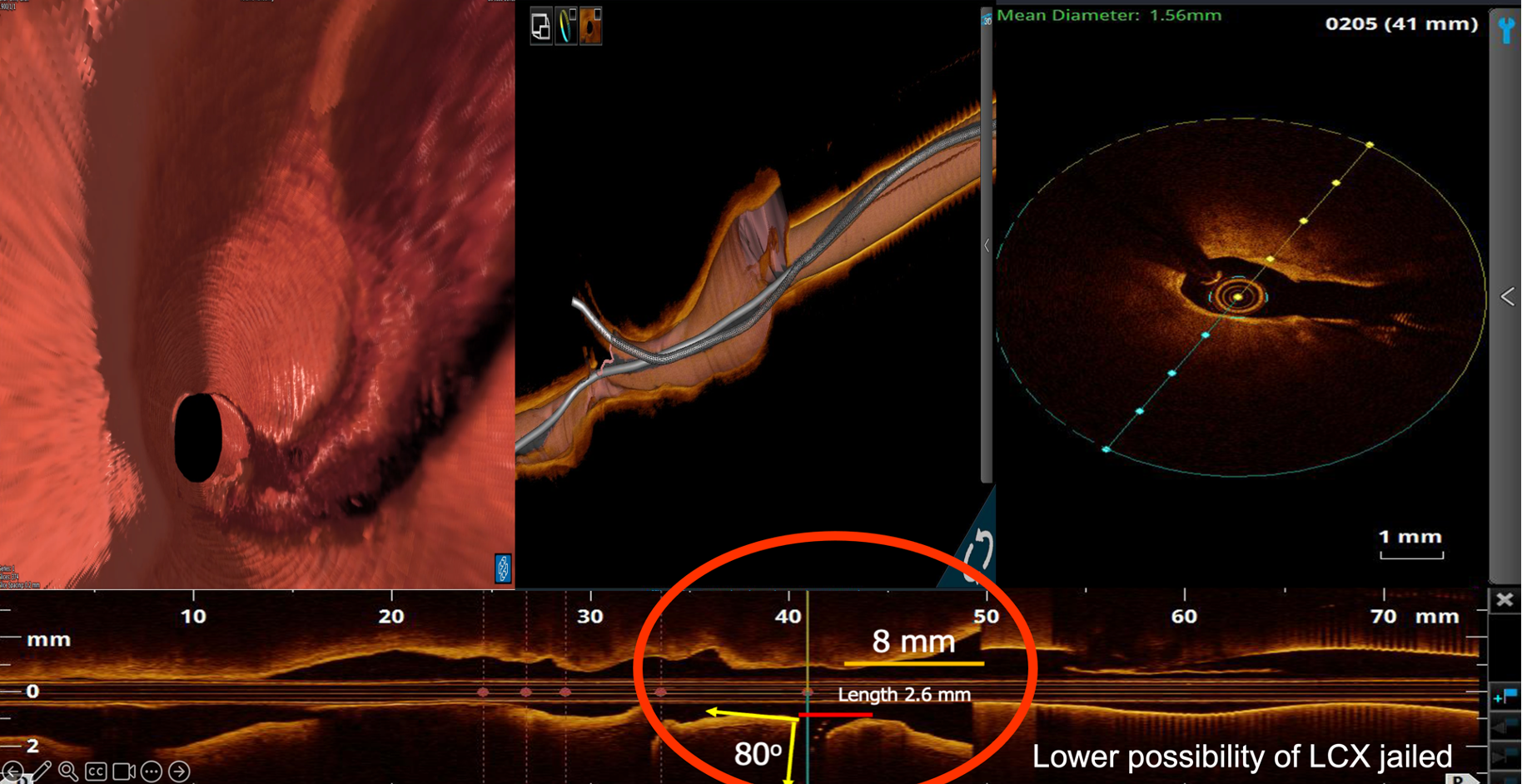
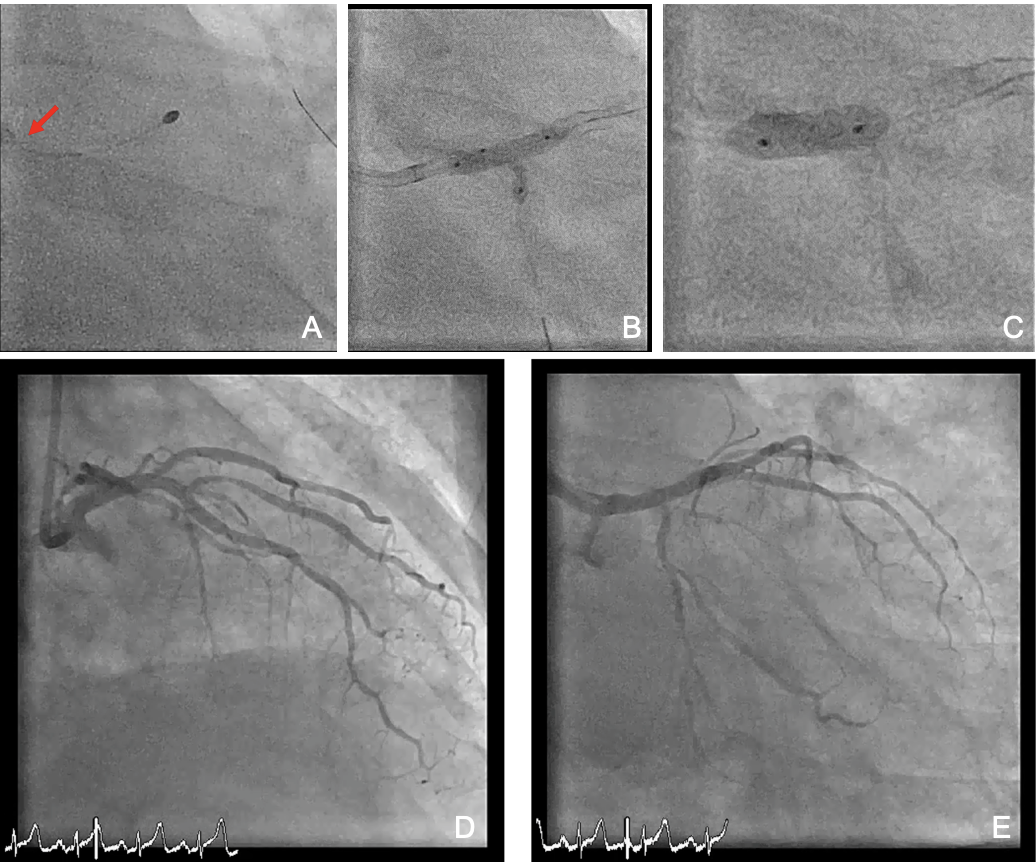
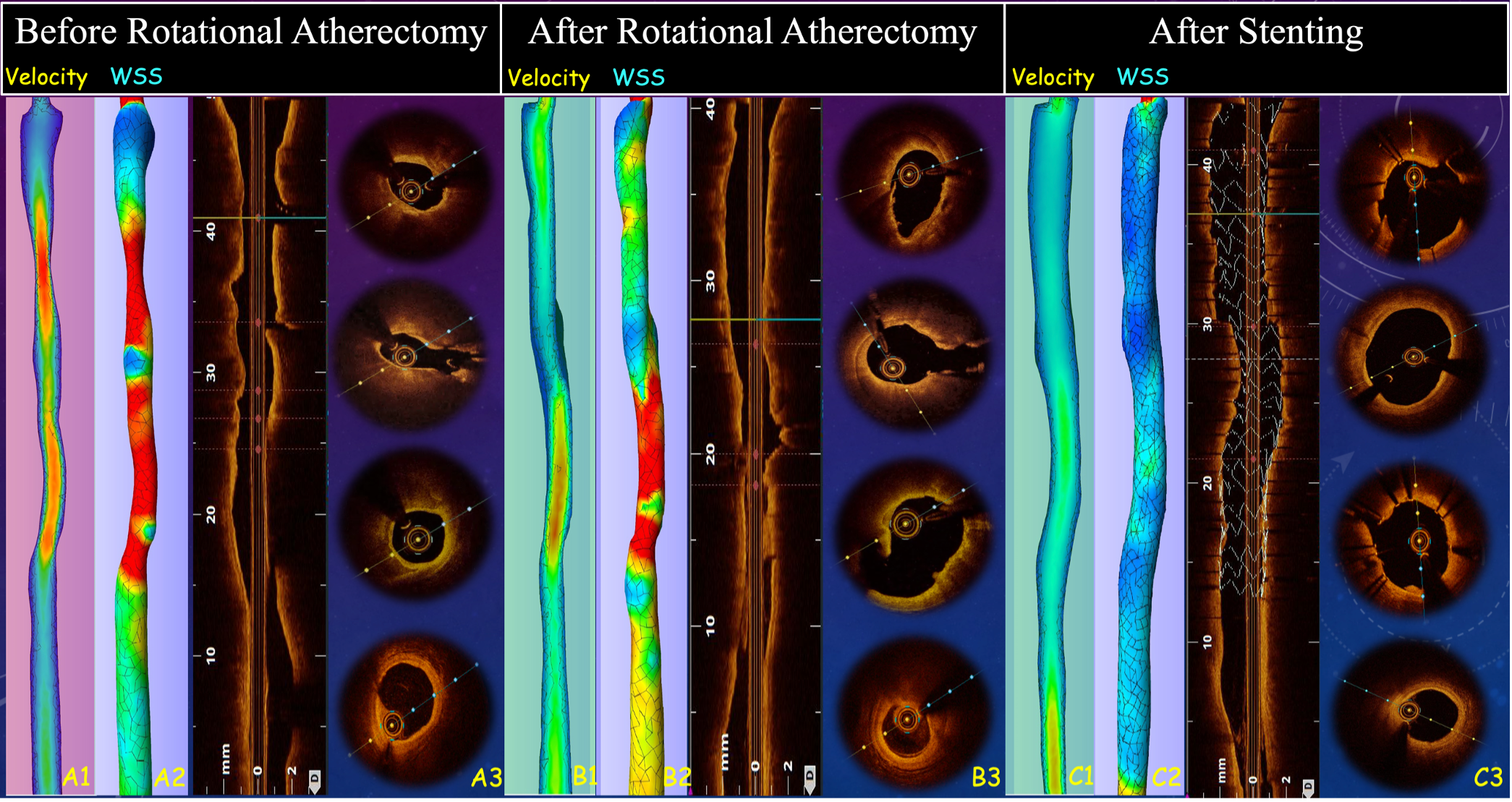



Case Summary
OCT has advantages on heavily calcified LM bifurcation PCI, providing information for calcium evaluation, visualization of GW crossing, stenting strategy, and stent optimization. We assessed OCT images of main vessel, side branch and reconstructed 3D geometry; decided doing RA with a 2.0 mm Rota burr and provisional stenting strategy. Post-processing CFD analysis provides information of bifurcation regional biomechanically related factors including flow velocity, pressure changes, and WSS, which are suggested as risk factors for developing CAD and future risk of in-stent restenosis and atherosclerosis. Application of CFD analysis for optimization of calcified bifurcation PCI is promising.

