Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-043
Optical Coherence Tomography Guided Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With Intravascular Lithotripsy After Failed Rotablation in a Severe Calcified Case
By Chon Seng Hong, Yu Min Lin
Presenter
Yu Min Lin
Authors
Chon Seng Hong1, Yu Min Lin1
Affiliation
Chi Mei Medical Center, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-043
Coronary - Complex PCI - Calcified Lesion
Optical Coherence Tomography Guided Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With Intravascular Lithotripsy After Failed Rotablation in a Severe Calcified Case
Chon Seng Hong1, Yu Min Lin1
Chi Mei Medical Center, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
This 64 years old male had history of 1. recurrent stroke with right hemiparesis and dysarthria 2. Left carotid stenosis 3. Hypertension 4. Dyslipidemia

He suffered from recurrent strokes and was transferred to our hospital for carotid intervention. He was a heavy smoker(1 PPD for 20 years). No chest discomfort, or dyspnea was noted before admission. Physical examination showed no jugular vein engorgement, bilateral clear breathing sounds, and regular heartbeats with no murmur.


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
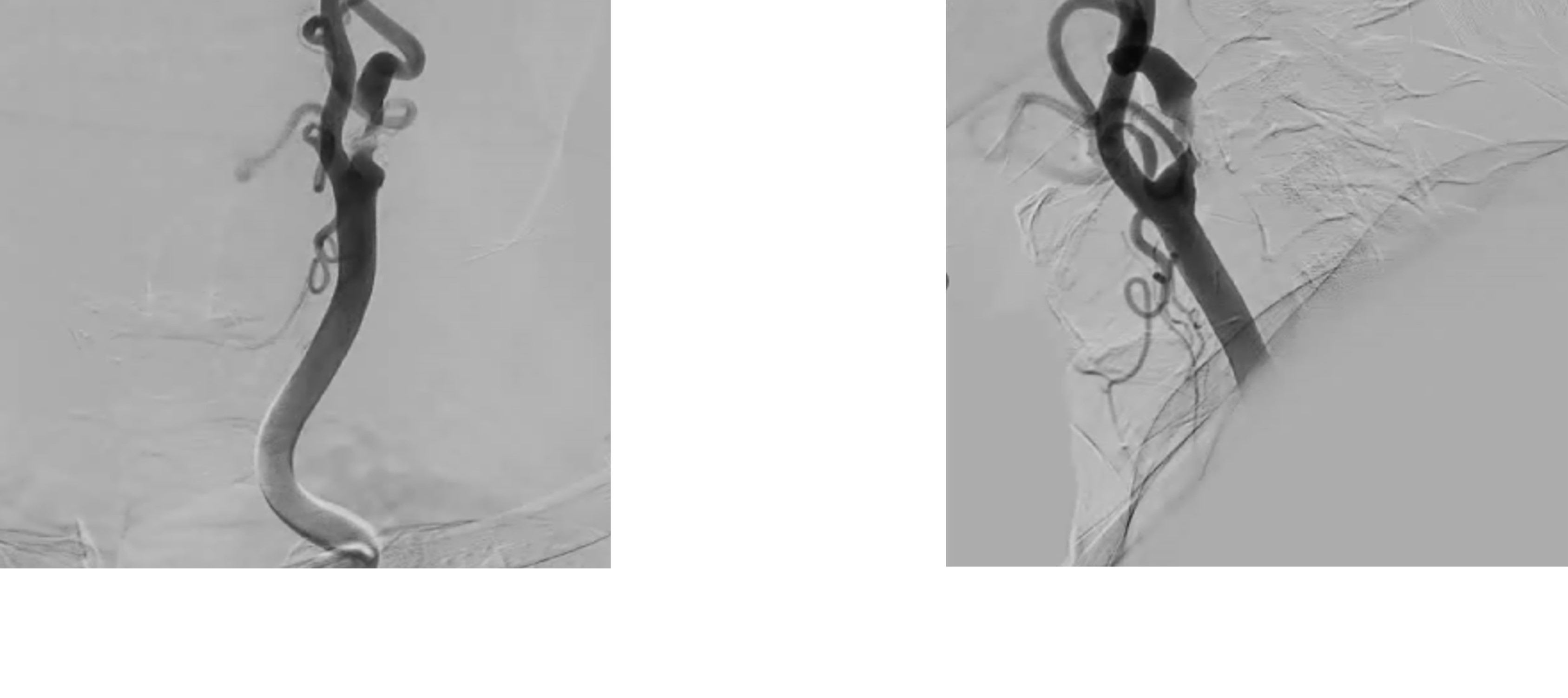
left carotid angiography was arranged which showed severe stenosis at left internal carotid artery.

Relevant Catheterization Findings
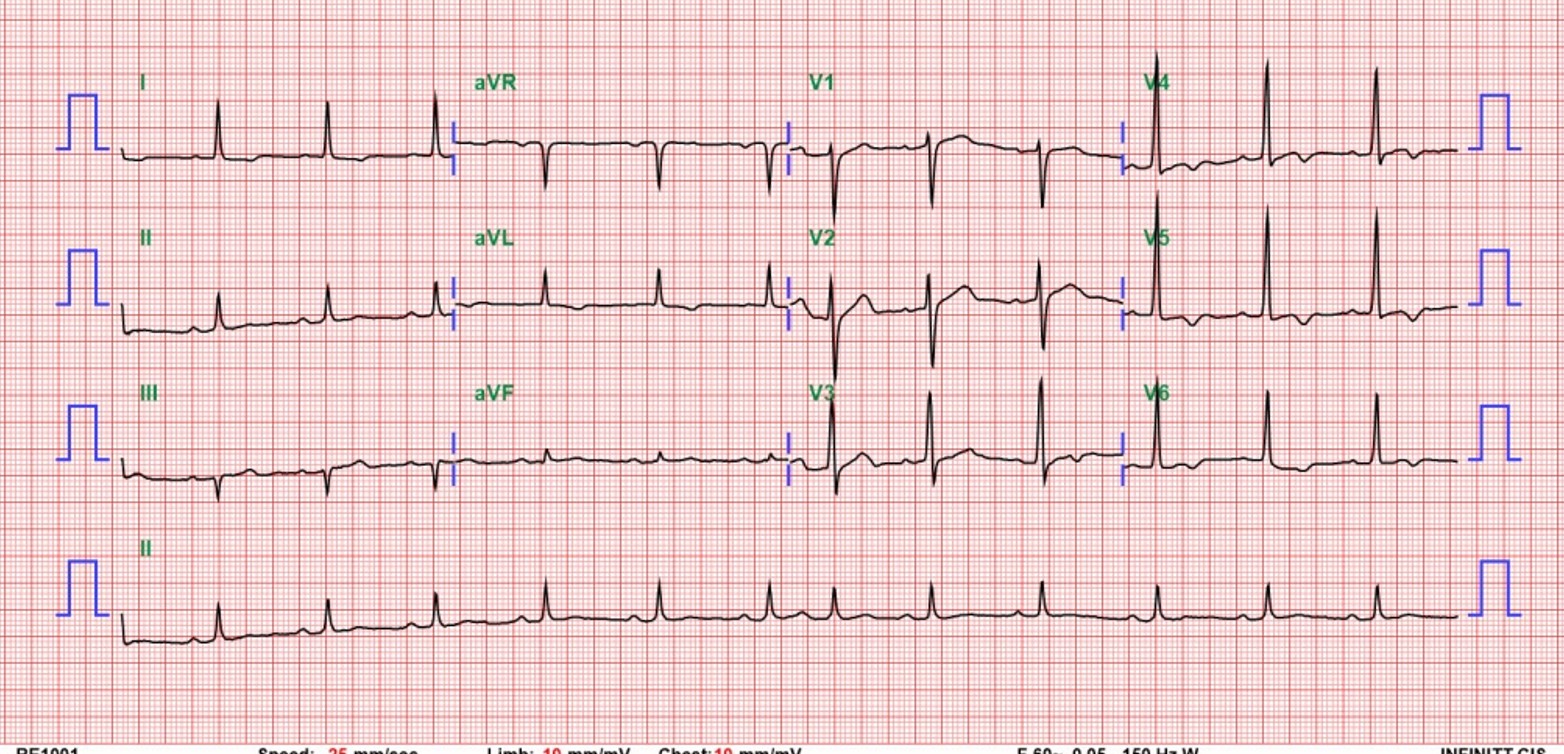
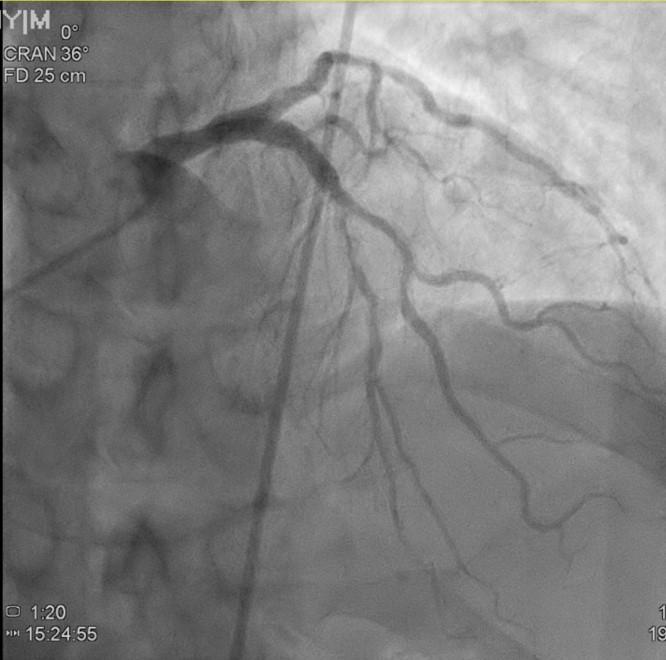
cardiac catheterization before carotid intervention showed diffuse left anterior descending artery calcified lesion, left circumflex distal significant stenosis, right coronary artery insignificant stenosis. Before intervention, we used IVUS for better leision evaluation which
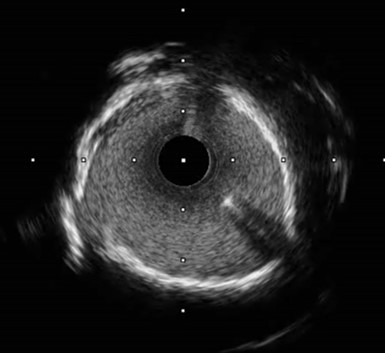

showed long ring calcification, and narrow minimal lumen diameter 1.73 mm.



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
At first, we used high pressure NC balloon but undilatable and exploded. Then we performed rotablation but rota burrs trapped twice and failed. After, cutting balloons were utilized but in vain.
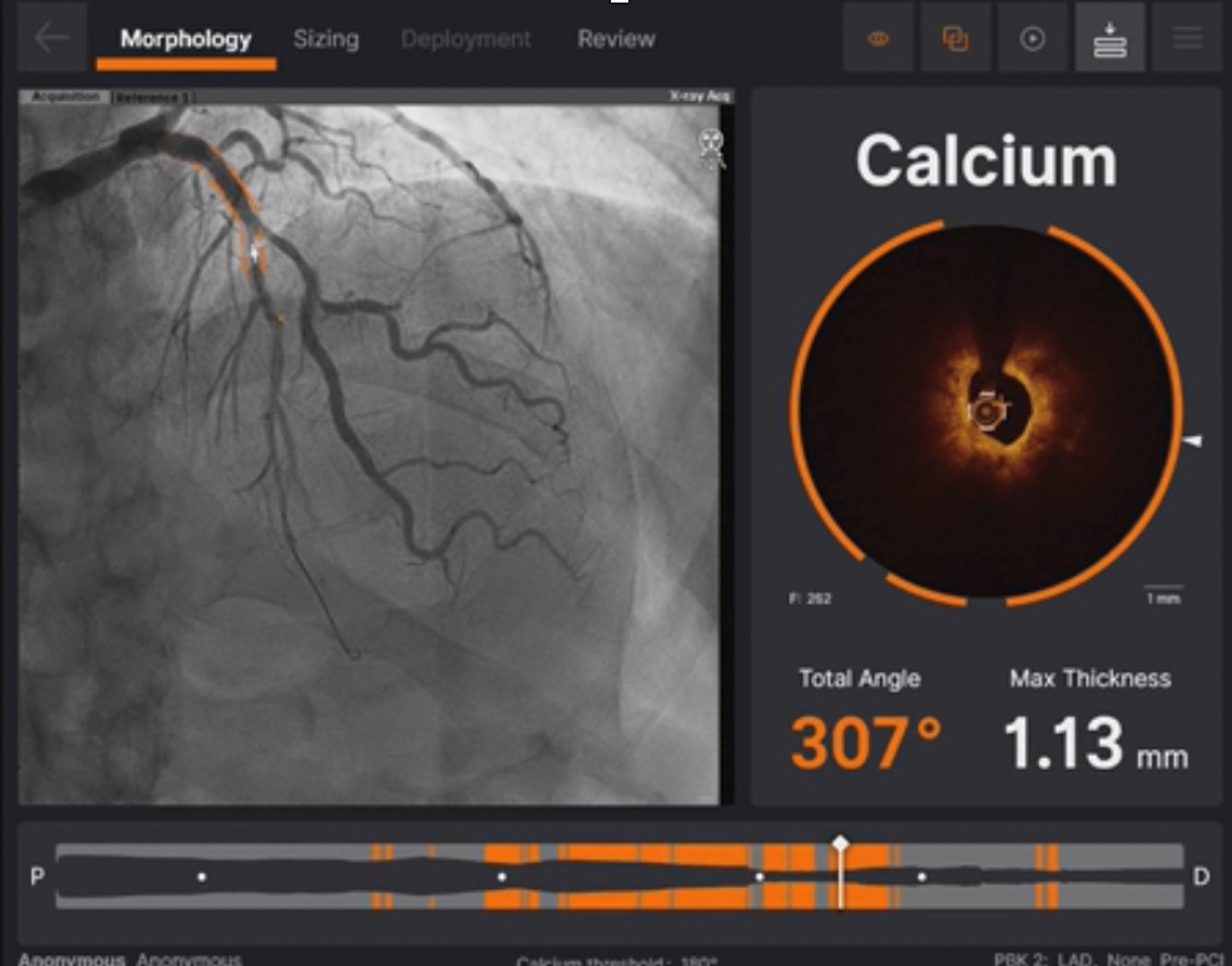

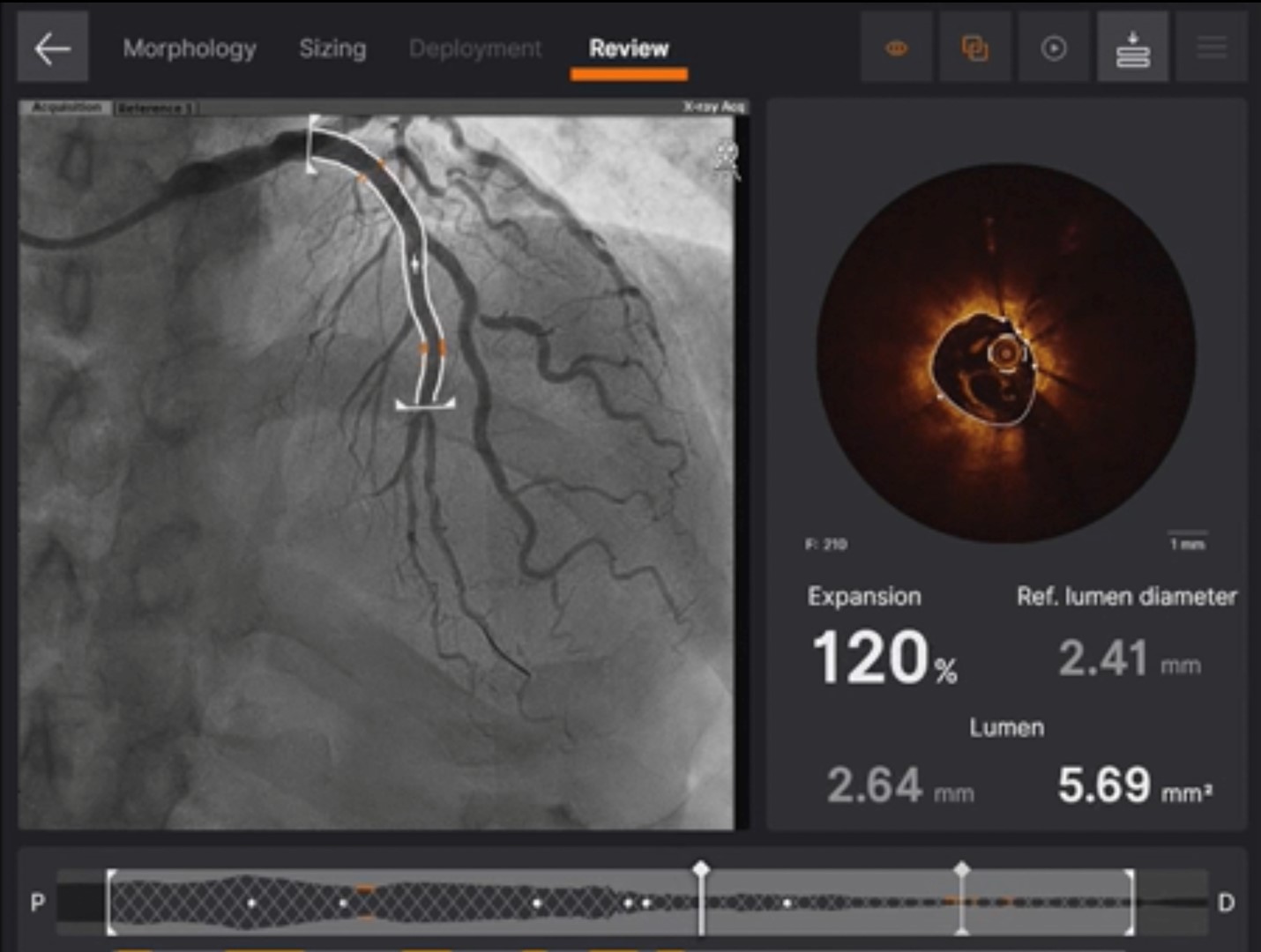
The first PCI failed and we arranged a staged intervention. To change strategy, we used OCT for better calcification evaluation and used Intravascular Lithrotripsy for plaque modification. Finally, we successfully fully dilated the calcified lesions with an NC balloon. At last, we used the mini crush two stent strategy and followed OCT for stent optimization. The final outcome looks good.



Case Summary
In complex PCI, calcified lesions can indeed be challenging, but we now have two powerful tools at our disposal. One of them is intravascular imaging, which can provide us with a lot more information for plaque evaluation. Within this, OCT, as compared to IVUS, offers a more in-depth analysis of calcification, particularly in terms of thickness. The second tool is Intravascular lithrotripsy, which can effectively address difficult calcified lesions.

