Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-136
How a Simple Absorbable Suture Saved a Life on Distal Wire Perforation
By Pangeran Akbar Syah, Neerusha Kaisbain, Chong Wei Loong, Houng Bang Liew
Presenter
Pangeran Akbar Syah
Authors
Pangeran Akbar Syah1, Neerusha Kaisbain2, Chong Wei Loong3, Houng Bang Liew2
Affiliation
Gunung Jati General Hospital, Cirebon, Indonesia, Indonesia1, Queen Elizabeth II Hospital, Malaysia2, KPJ Sabah Specialist Hospital, Malaysia3,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-136
Coronary - Complication Management
How a Simple Absorbable Suture Saved a Life on Distal Wire Perforation
Pangeran Akbar Syah1, Neerusha Kaisbain2, Chong Wei Loong3, Houng Bang Liew2
Gunung Jati General Hospital, Cirebon, Indonesia, Indonesia1, Queen Elizabeth II Hospital, Malaysia2, KPJ Sabah Specialist Hospital, Malaysia3,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 55 years old woman with underlying diabetes and hypertension presented to our emergency department 16 hours after onset of typical chest pain. Patient was hemodynamically stable. 12-lead ECG showed sinus rhythm with ST segment elevation and pathological Q wave on anterior leads.
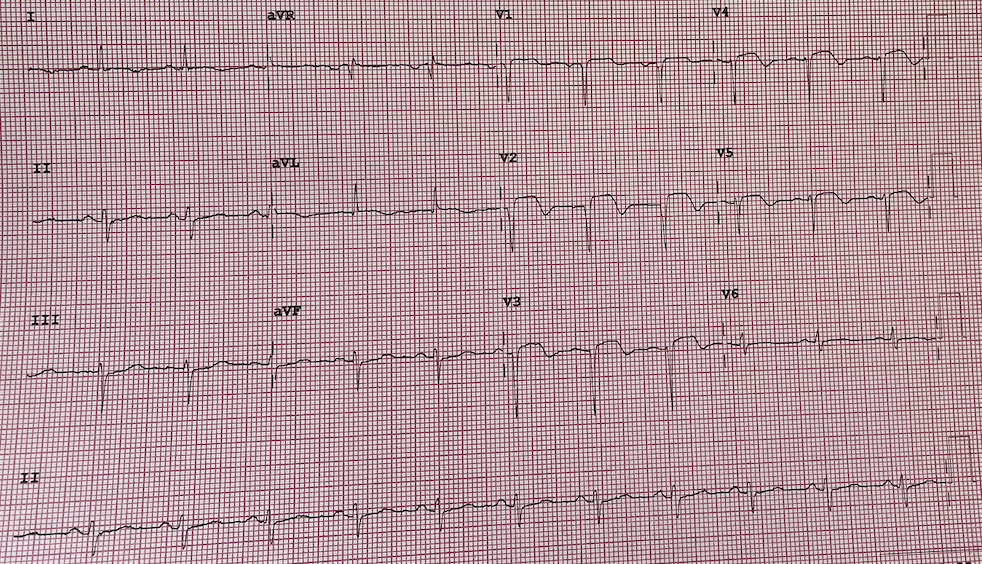

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Blood investigation : hemogloblin 13 g/dL, Urea 3.5 mmol/L,Troponin I 3240.8 ng/mL, Creatinine 36 mmol/L. Echocardiography showed reduced left ventricular systolic function (EF 30%), hypokinetic at anterior and apical wall, with normal valves.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiogram showed right dominant, normal left main, total occlusion on the proximal part of left anterior descending artery. Normal circumflex, and mild disease in the proximal part of right coronary artery, total occlusion on the ostial posterior left ventricular artery.
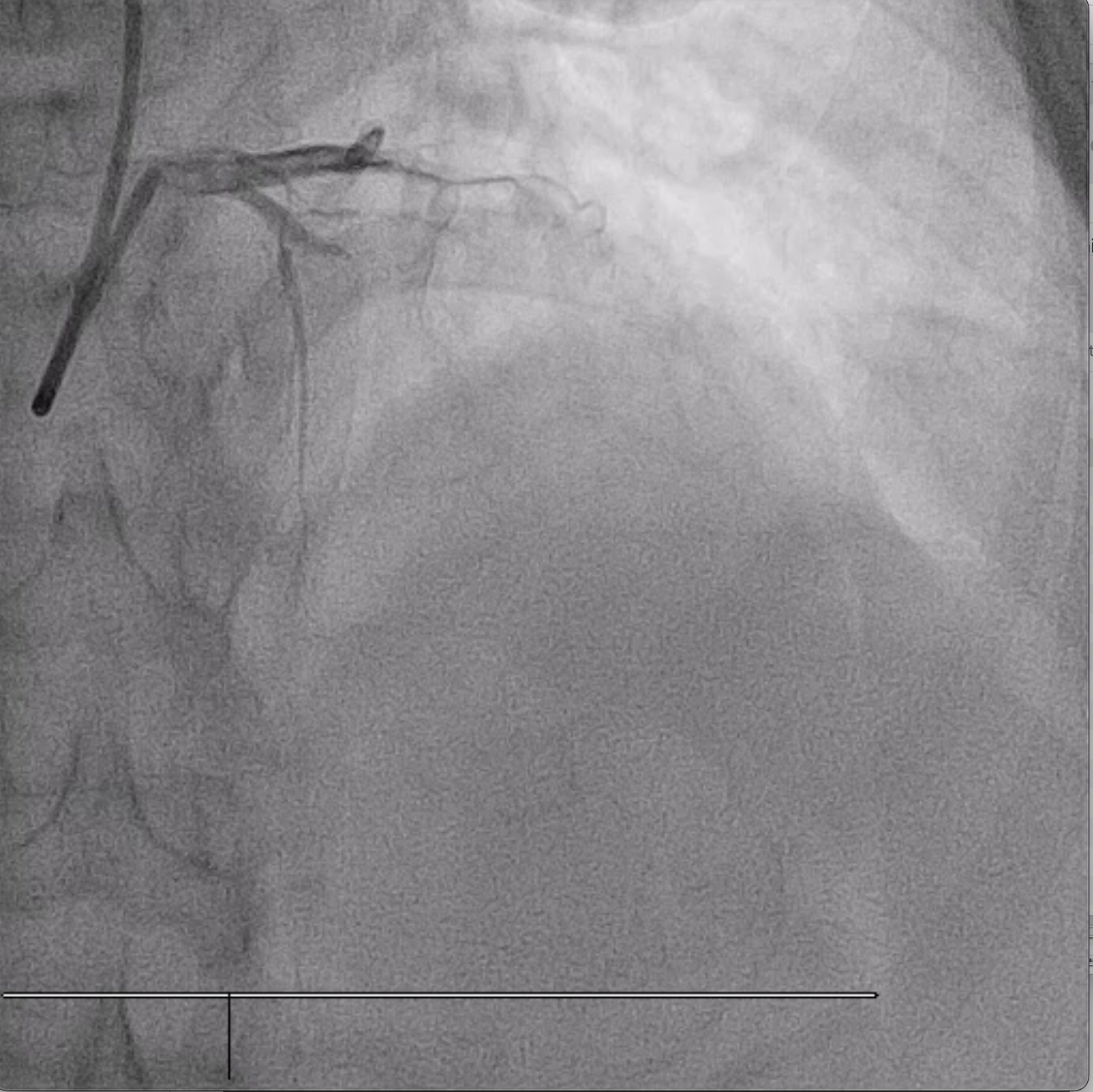

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Coronary angioplasty was performed via right radial access with guiding catheter Extra Back Up 3.5/6Fr. A Balance Middle Weight guidewire was unable to cross the lesion in the left anterior descending artery, however Pilot 50 guidewire was successfully passed into distal left anterior descending artery. Mid to proximal left anterior descending artery was predilated with Euphora non-compliant coronary balloon 2.5 x 15 mm at 14 atm. Two drug eluting stents ( Biofreedom Ultra 2.5 x 24 mm and Biofreedom Ultra 3.0 x 24mm) were deployed at proximal to mid left anterior descending artery. Post dilated it with Sapphire non-compliant coronary balloon 3.0 x 12 mm at 18 atm. At this point, noted there was a perforation in the distal left anterior descending artery. Inflated Sapphire non-compliant coronary balloon 2.0 x 15 mm at 4 atm at distal left anterior descending artery. Fine Cross micro catheter with Balance Middle Weight guidewire were passed to distal left anterior descending artery. Four pieces of 2-3 mm segments of absorbable sutures (Vicryl 3.0) were injected via Fine Cross micro catheter to distal left anterior descending artery, the procedure steps repeated another time. Post procedure showed residual perforation. Repeated echocardiography 6 hours after the procedure showed no pericardial effusion. Patient was discharged well the next day.

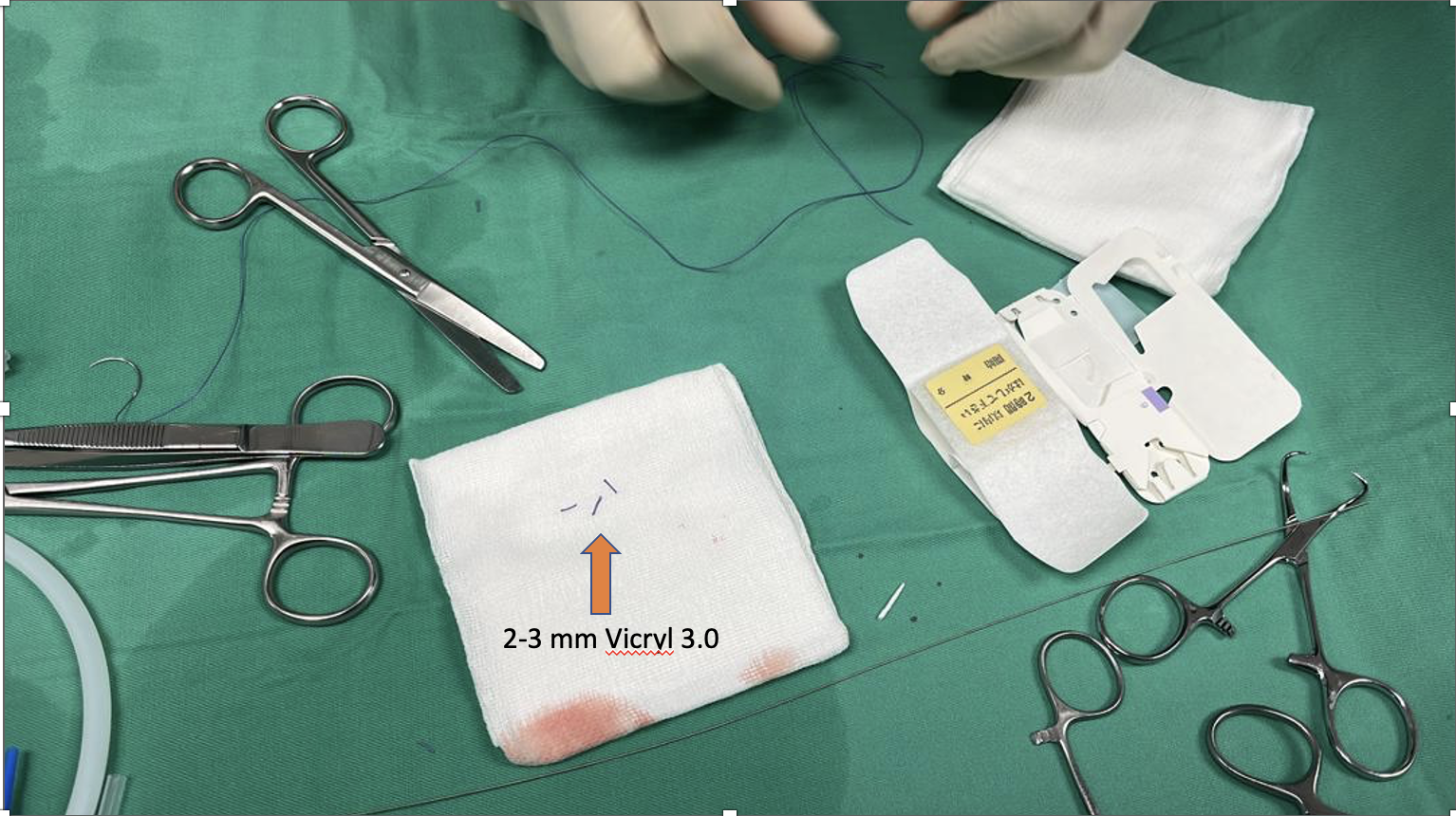




Case Summary
Coronary artery perforation is an uncommon but highly dangerous complication of PCI that can lead to significant mortality and morbidity if not promptly identified and treated. The most common cause of distal perforation is related to distal wire migration in a distal small caliber branch, hence constant attention to guidewire is very important. Absorbable suture embolization seems to be reasonable alternative strategy to control distal or small vessel coronary artery perforation.

