Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-024
Effects of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Load in a Tertiary Centre
By Vanessa Hwee Ting Tey, Eran Wen Jun Sim, Cliff Li, Hee Hwa Ho
Presenter
Vanessa Hwee Ting Tey
Authors
Vanessa Hwee Ting Tey1, Eran Wen Jun Sim1, Cliff Li1, Hee Hwa Ho1
Affiliation
Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore1
View Study Report
TCTAP A-024
Clinical Trials & Science
Effects of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Load in a Tertiary Centre
Vanessa Hwee Ting Tey1, Eran Wen Jun Sim1, Cliff Li1, Hee Hwa Ho1
Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore1
Background
The COVID-19 pandemic brought about strict control measures and changing mindsets towards hospital admissions with a sway of aversion towards healthcare visits. We looked at the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the number of patients admitted to our hospital for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) during the height of the COVID pandemic in 2022.
Methods
We accessed our PCI registry for the year 2022 and looked at the number of inpatient PCI procedures. These included patients who presented with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) as well as patients with stable ischemic heart disease. We then obtained the number of locally reported COVID cases from the World Health Organization (WHO) registry and compared them to our centre’s tertiary registry.
Results
The highest number of reported COVID cases occurred in February 2022 at 434998 and the number of PCI cases in the same month was the lowest at 61. The lowest number of reported COVID cases occurred in December 2022 at 30825 and the number of PCI cases in the same month was the highest at 119. Table 1 shows the monthly number of reported COVID cases in Singapore superimposed on the number of PCI cases in our centre. There was no temporal trend to the number of COVID cases within the year, but the number of PCI cases increased from January to December. Negative correlation coefficient calculated was however only -0.49.
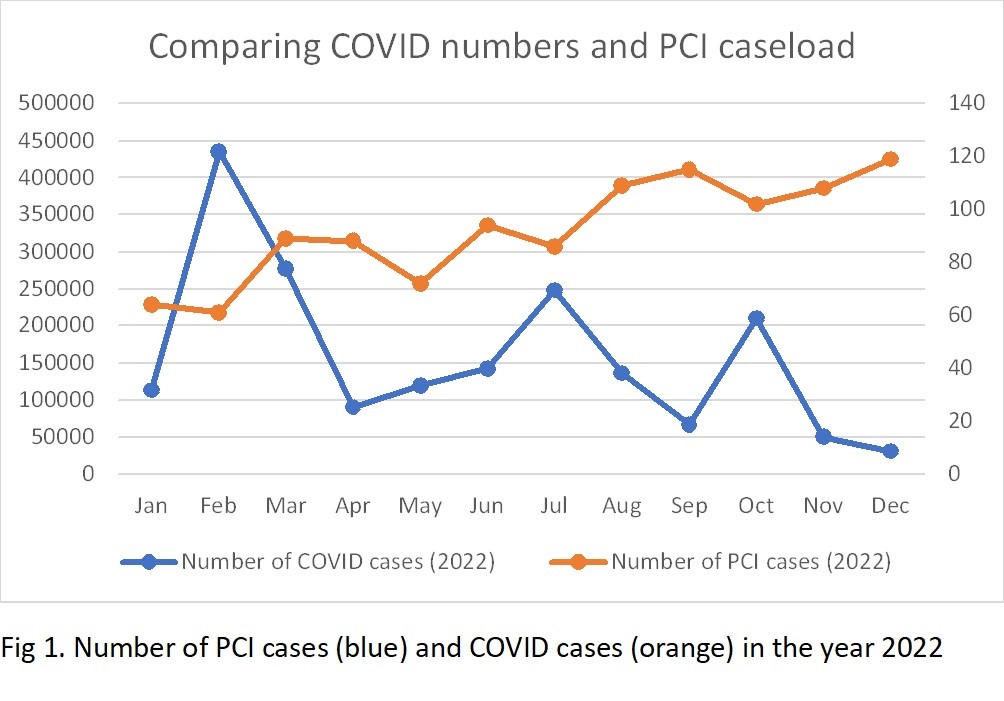

Conclusion
The trends of reduced PCI volumes during the COVID pandemic have been reported and the number of PCI cases in our centre appear to reflect reduction of PCI cases when there is a surge in reported COVID infections. This occurred despite our centre being equipped to perform PCI in a safe isolated environment for COVID positive patients. One of the main reasons could be that of aversion towards healthcare visits and avoidance of the hospital. We also noted that the number of PCI cases increased in the subsequent month after the increased reported COVID cases and this could perhaps reflect the delayed presentation of prothrombotic sequelae after a COVID infection.

