Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
ABS20191113_0004
| Basic Science, Animal Models and Preclinical Studies | |
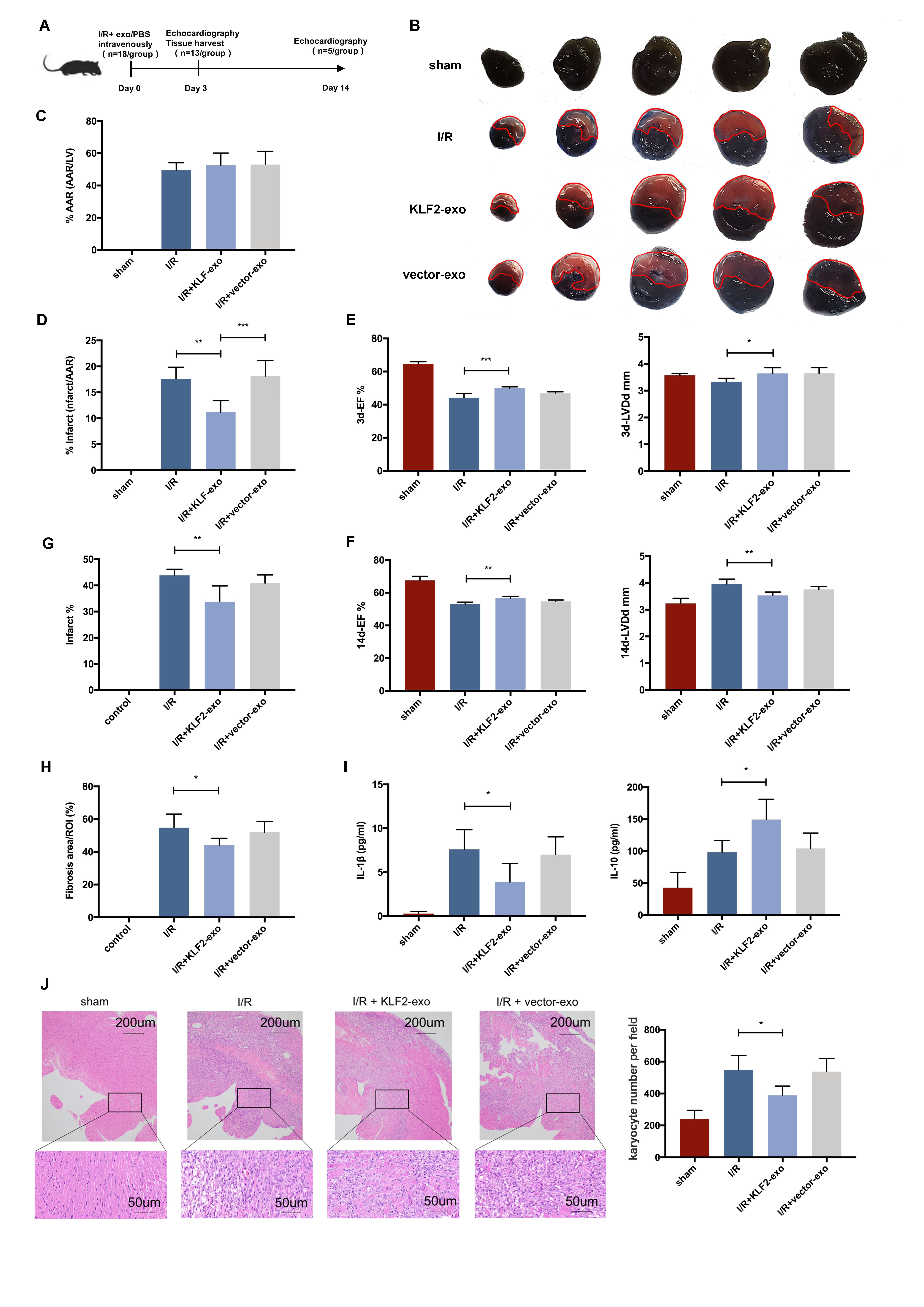
| Exosomes Derived from Krüppel-Like Factor 2 Overexpressed Endothelial Cells Attenuate Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Preventing Ly6Chigh Monocytes Recruitment | |
| Shuaihua Qiao1, Jun Xie2 | |
| Nanjing University, China1, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, China2 | |
|
Background:
Krüppel-like factors (KLF2)as a transcription factor, which high expression in endothelial cells (ECs) under laminar flow, could confer anti-inflammatory effects in cells. After I/R injury in myocardium, ECs with pro-inflammatory phenotype play an important role in monocyte activation and recruitment. Exosomes from ECs is an important cellular signal transduction medium in this ischemic related inflammatory process. Whether the exosomes from EC with anti-inflammatory phenotype could prevent monocyte activation and recruitment needs to be explored. Here we prepared the exosomes from KLF2-overexpression ECs (KLF2-Exo), and uncover its immunomodulatory role in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R).
|
|
|
Methods:
We transduced HUVECs with a lentiviral vector encoding KLF2, and exosomes were isolated from thesupernatant using gradient centrifugation method. Mice underwent 45-min ischemia, followed by reperfusion, and KLF2-Exo was administrated to mice through intravenous injection. The infarct size was assessed by Evan¡¯s blue/TTC staining. Heart function was assessed by UCG. Immune cell filtration and inflammation were examined by flow cytometry, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, and immunohistochemistry.
|
|
|
Results:
We demonstrated that KLF2 expression was increased in HUVECs under laminar flow. Administration of KLF2-Exo after myocardial I/R could ameliorate I/R injury and alleviate inflammation level in heart and serum. Systemic depletion of macrophages with clodronate liposomes abolished the curative effects of KLF2-Exo while splenectomy has no significant alteration. KLF2-Exo diminished Ly6chigh monocytes, not Ly6clowmonocytes, among myocardium, peripheral blood and spleen reservoir, which was associated with suppression of monocyte recruitment in the bone marrow. In vitro study, we detected KLF2-Exosignificantly inhibited the migration of Ly6chighmonocytes, resulting from the reduced expression of C-C chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2). miRNA-sequencing ofKLF2-Exo and bioinformatics analysis implicated miR-24-3p as a potent candidate mediator of monocytes recruitment and CCR2 as a downstream target. miR-24-3p mimic obviously inhibited the migration of Ly6chigh monocytes and miR-24-3p antagomir reversed the effect of KLF2-Exo in myocardial I/R.
 |
|
|
Conclusion:
Ou rdata indicates that KLF2-Exo attenuates myocardial I/R injury in mice via shuttling miR-24-3p that restrain the Ly6chighmonocytes recruitment. This study sheds new light on the application of exosomes as a potential therapeutic tool for myocardial I/R injury.
|
|