Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
ABS20191030_0010
| Acute Coronary Syndromes (STEMI, NSTE-ACS) | |
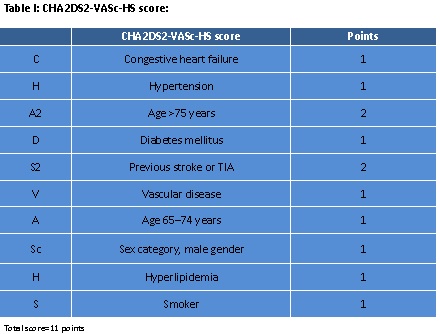
| Association of CHA2DS2-VASc-HS Score with Adverse In-hospital Outcomes in Patients with Non-ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction | |
| Poppy Bala1 | |
| Evercare Hospital Dhaka, Bangladesh1 | |
|
Background:
Patients with NSTEMI typically have more commodities and long-term mortality. Early detection of adverse in-hospital outcomes is important for the therapeutic decision of patients with NSTEMI. Recently it was described that CHA2DS2-VASc-HS and CHA2DS2-VASc score are a predictor for severity and adverse in-hospital outcomes in patients with SCAD and ACS. The aim of our study was to assess the accuracy of the CHA2DS2-VASc-HS score predicting adverse in-hospital outcomes in NSTEMI patients.
|
|
|
Methods:
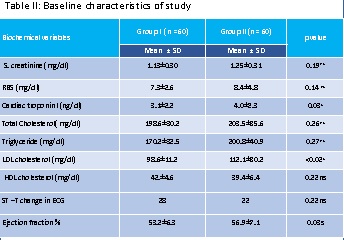
This was a Prospective cohort study performed over a period of 1 year from September, 2016 to September, 2017 at Department of Cardiology, National Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Dhaka. Total 120 patients with NSTEMI were selected by purposive sampling technique based on predefined enrollment criteria. Then the CHA2DS2-VASc-HS score was calculated and the study subjects were divided into two groups. Patients¡¯ with the CHA2DS2-VASc-HS score>4 put into group I and score¡Â 4 into group II. Then in-hospital outcomes were observed and recorded. Multivariate regression analysis was done to find predictors of in-hospital mortality.
  |
|
|
Results:
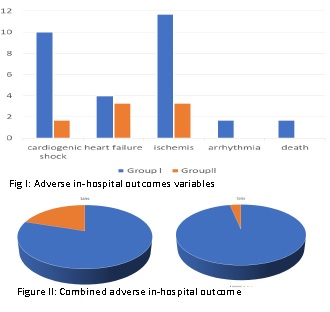
It was observed that, patients withCHA2DS2-VASc-HS score >4 had more adverse in-hospital outcomes than CHA2DS2-VASc-HS score¡Â 4 (20% vs 3.3%, p=0.01). Group I patients developed cardiogenic shock 10%,heart failure 4%, recurrent ischemia 11.7%, significant arrhythmia 1.7% and death 1.7% than group II patients (1.7%, 3.3%, 3.3%, 0% and 0% respectively). By risk measurement, CHA2DS2-VASc-HS score>4 emerged as a risk factor for developing adverse in-hospital outcome (Relative risk=6).
  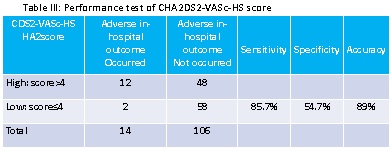 |
|
|
Conclusion:
NSTEMI patients with high CHA2DS2-VASc-HS score have more adverse in-hospital outcomes. This score, which involves only clinical parameters, can be used as a predictor of outcomes in this group of patients.
|
|