Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-033
Erased - Crossing the Uncrossable
By Anuj Kapadia, Pragathi Gurram, Rajeev Menon, Swaroop Bharadi
Presenter
Anuj Kapadia
Authors
Anuj Kapadia1, Pragathi Gurram1, Rajeev Menon1, Swaroop Bharadi1
Affiliation
AIG Hospitals, India1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-033
Coronary - Adjunctive Procedures (Thrombectomy, Atherectomy, Special Balloons)
Erased - Crossing the Uncrossable
Anuj Kapadia1, Pragathi Gurram1, Rajeev Menon1, Swaroop Bharadi1
AIG Hospitals, India1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
75 year male, known Diabetic, Hypertensive with history suggestive of exertional angina for 2 weeks NYHA FC II, with no other associated symptoms. Initial assessment showed normal hemodynamics, normal cardiovascular findings, clear lungs and patient was not in heart failure.


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
His ECG showed normal sinus rhythm, no major ST - T changes. 2D Echo showed, normal biventricular function, mild concentric LVH, with grade I diastolic dysfunction and normal valves. Troponin - I was negative. HB was 14.8 gm/dl, creatinine was 0.9 mg/dl. He was diagnosed as CAD - ACS - Unstable angina. Hence was taken for conventional coronary angiography.
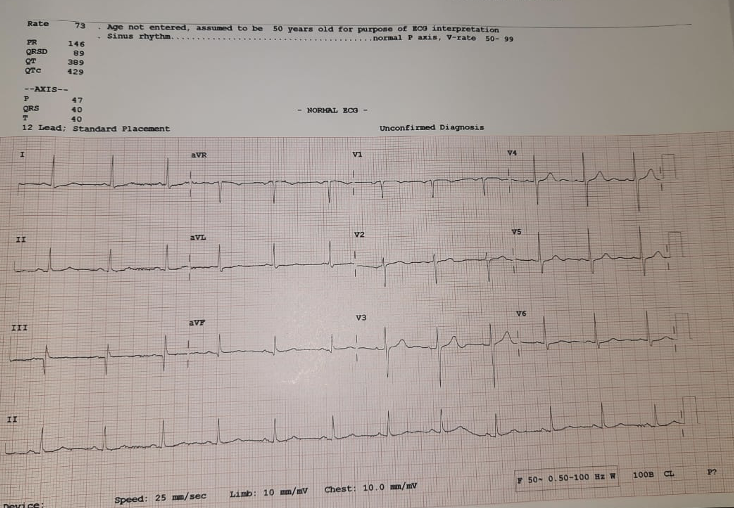

Relevant Catheterization Findings
His CAG revealed ostial RCA discrete narrowing with calcium nodule and luminal narrowing to 99% stenosis followed by long segment mild disease with distal TIMI II flow. Left systemshowed calcified vessels with mild plaquing in proximal LAD. Left system giving Grade II Rentrop collaterals to RCA filling it faintly. In view of severe calcification causing luminal narrowing, it is planned for upfront ROTABLATION for plaque modification with extra support rota wire and TPI backup.
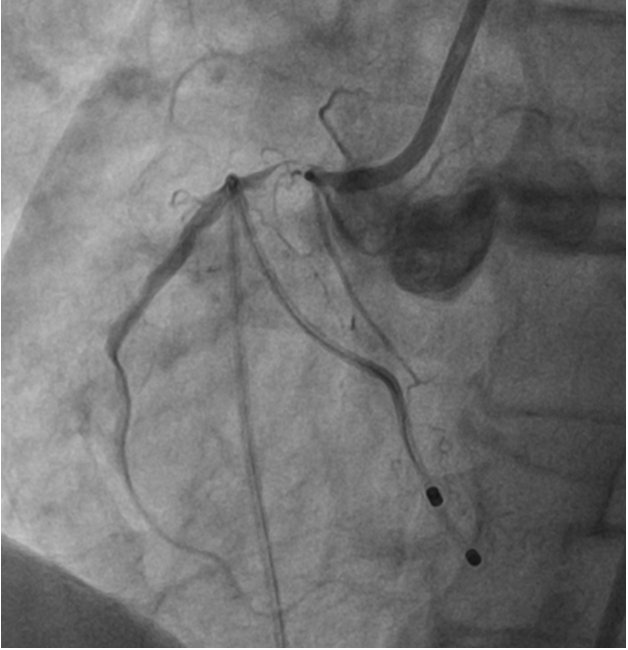
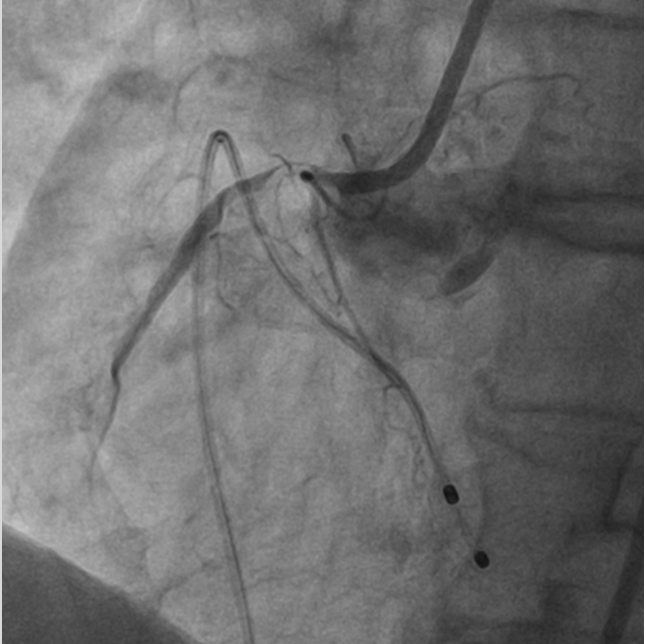


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
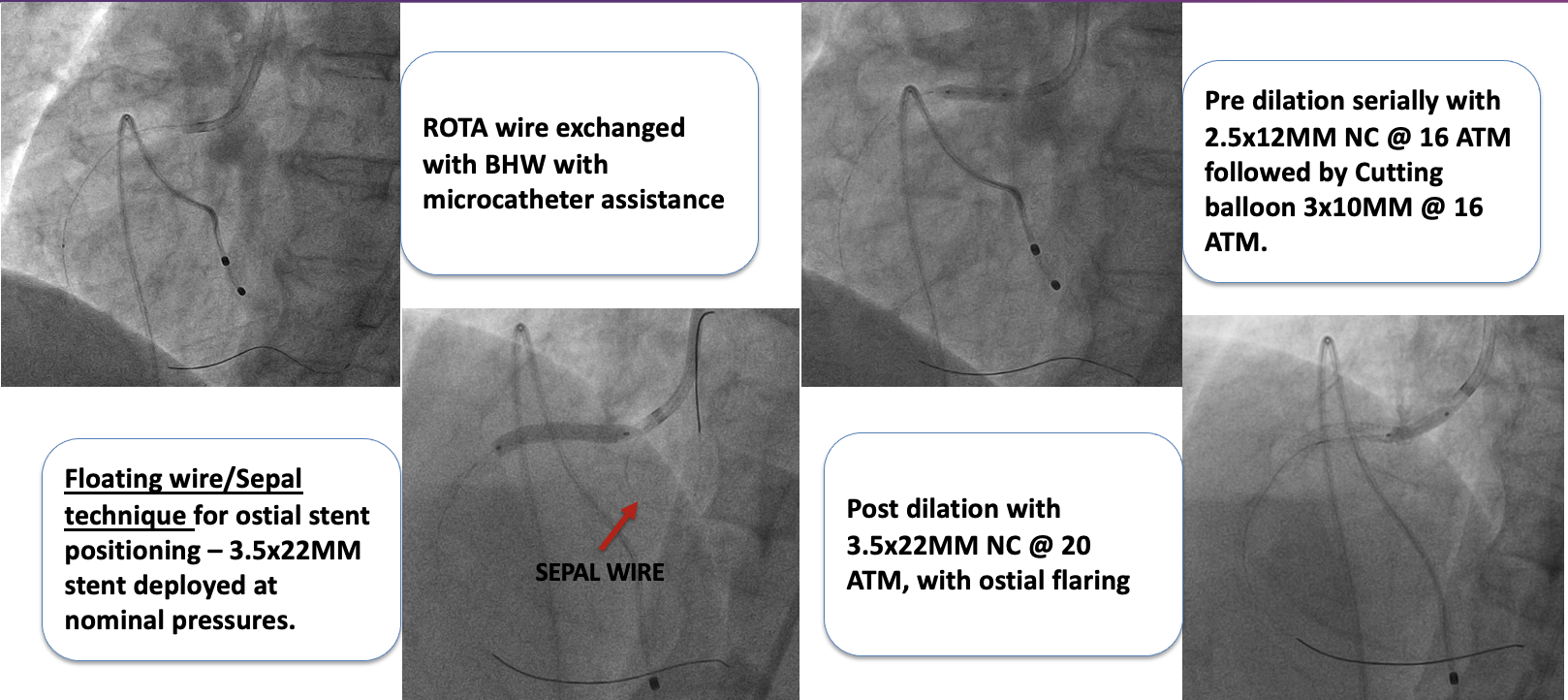
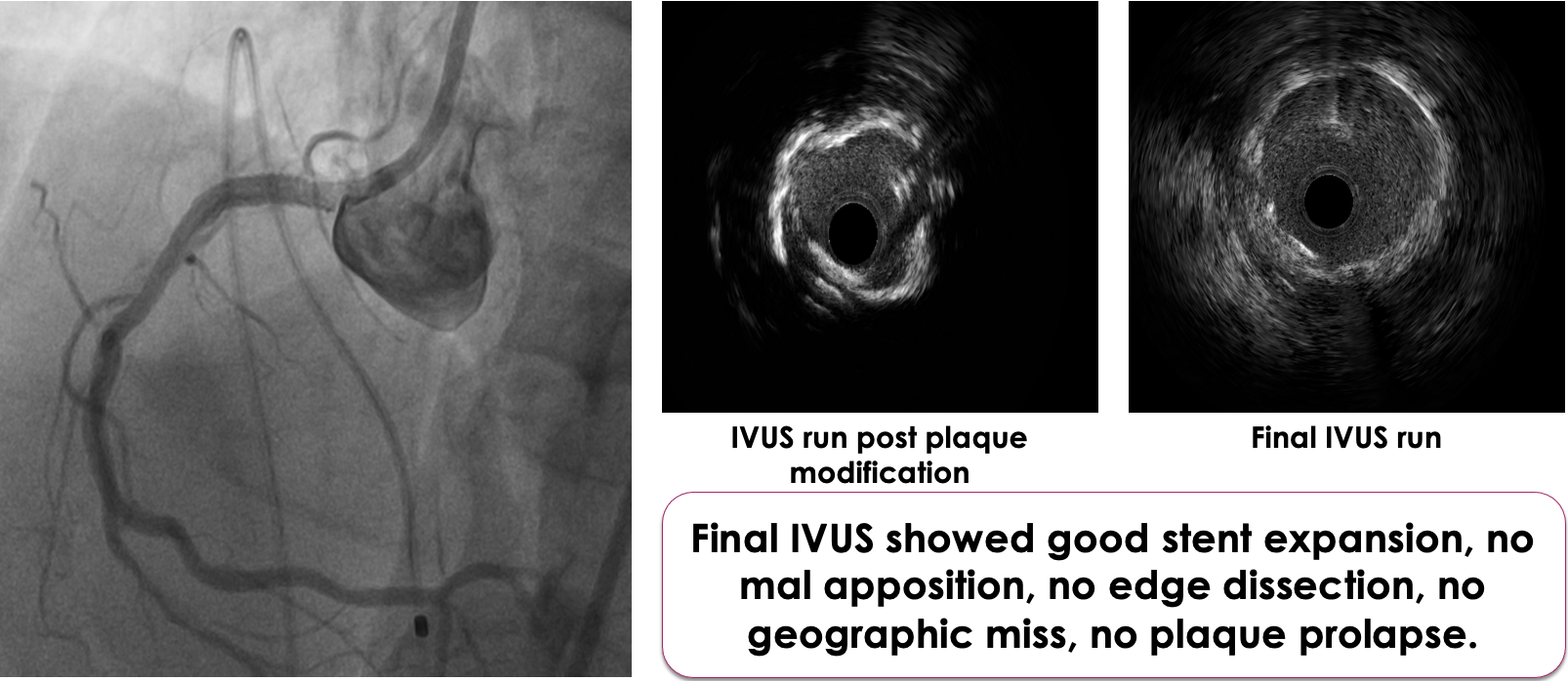
6 F JR 3.5 is chosen as the guide catheter through right radial approach. Lesion could not be crossed with work horse wire hence Gaia 1 used. But microcatheter or nic nano balloon could not cross the lesion. Hence Lasing done with 0.9 MM ELCA Laser catheter for microcatheter or balloon uncrossable lesion. The system calibrated at 40 mJ/mm^2 at 40 Hz. On encountering resistance these default settings are increased in a stepwise fashion to 80 mJ/ 80 Hz which could lase the calcium. After lasing, microcatheter could cross the lesion. Extra support ROTA wire chosen in view of ostial calcific nodule. Gaia 1 exchanged with ROTA wire with microcatheter assistance. Later Rotablation done with 1.5MM Rota burr with TPI back up. After ablation ROTA wire is exchanged with BHW. Pre dilated serially with 2.5 x 12 MM NC @ 16 ATM followed by Cutting balloon 3 x 10 MM @ 16 ATM. “Floating wire/Sepal technique” is used for ostial stent positioning – 3.5 x 22 MM stent was deployed at nominal pressures ensuring ostial coverage. Post dilated with 3.5 x 22 MM NC @ 20 ATM, with ostial flaring. Final IVUS showed good stent expansion, no mal apposition, no edge dissection, no geographic miss, no plaque prolapse. Final angiography showed distal TIMI III flow.
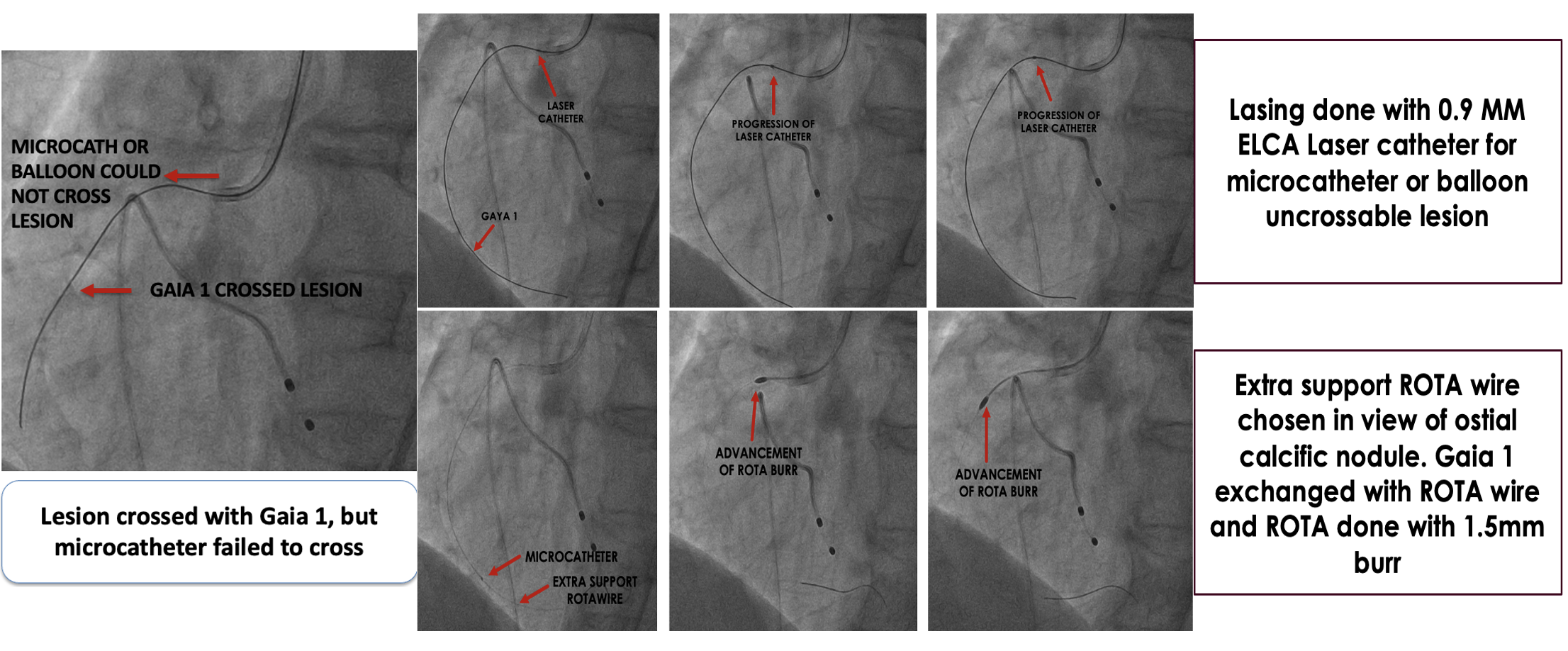



Case Summary
Adequate Plaque modification is of prime importance in calcific lesions, as calcium hampers delivery of equipment and adequate stent expansion. In balloon or microcatheter uncrossable lesions, LASING helped in softening the calcium adequate enough to deliver microcatheter.


