Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-010
Outcomes in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With DynamX Bioadaptor Scaffold
By Huan Yean Kang, Kai Soon Liew, Chai Yih Tan, Nancy Virginia, Prabahkar Subramaniam, Mohd Khairi Othman, Kenneth Khoo Kay Leong, Saravanan Krishinan, Kantha Rao Narasamuloo, Manan Pareek, Chee Tat Liew, Dharmaraj Karthikesan
Presenter
Huan Yean Kang
Authors
Huan Yean Kang1, Kai Soon Liew1, Chai Yih Tan1, Nancy Virginia1, Prabahkar Subramaniam1, Mohd Khairi Othman1, Kenneth Khoo Kay Leong1, Saravanan Krishinan1, Kantha Rao Narasamuloo1, Manan Pareek2, Chee Tat Liew3, Dharmaraj Karthikesan1
Affiliation
Hospital Sultanah Bahiyah, Malaysia1, Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark2, Pantai Hospital Penang, Malaysia3
View Study Report
TCTAP A-010
ACS/AMI
Outcomes in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With DynamX Bioadaptor Scaffold
Huan Yean Kang1, Kai Soon Liew1, Chai Yih Tan1, Nancy Virginia1, Prabahkar Subramaniam1, Mohd Khairi Othman1, Kenneth Khoo Kay Leong1, Saravanan Krishinan1, Kantha Rao Narasamuloo1, Manan Pareek2, Chee Tat Liew3, Dharmaraj Karthikesan1
Hospital Sultanah Bahiyah, Malaysia1, Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark2, Pantai Hospital Penang, Malaysia3
Background
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using a bioadaptor scaffold offers a novel approach for managing acute coronary syndrome (ACS). The scaffold features uncaging elements that restore vessel function and enhance vessel remodelling after resorption of its biodegradable polymer coating which may be beneficial for addressing vasospasm in ACS patients. This study evaluates the safety and outcomes of ACS patients treated with the bioadaptor scaffold.
Methods
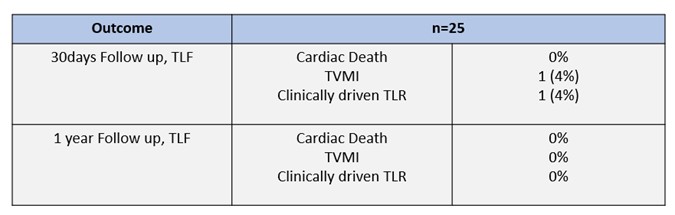
We conducted a retrospective observational study of consecutive ACS patients who underwent PCI using the bioadaptor scaffold at the index procedure from January 2021 to January 2024 at a single centre. The outcome was target lesion failure (TLF), defined as a composite of cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction, and clinically driven target lesion revascularization at 30 days and at18 months, respectively.
Results
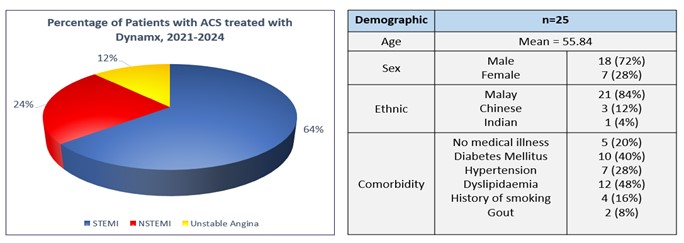
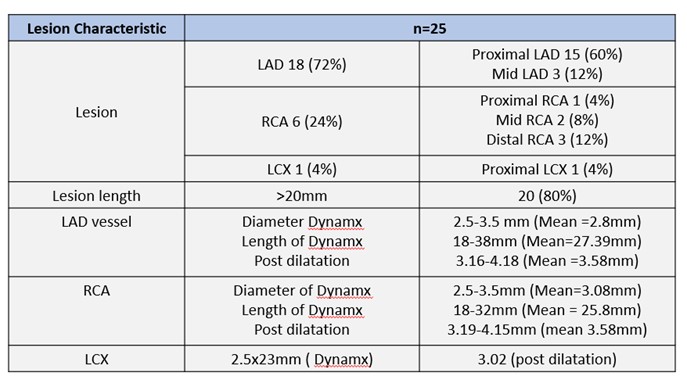
The study included 25 ACS patients treated with the bioadaptor scaffold, with a mean age of 55.84 years; 72% were male. The majority were of Malay ethnicity (72%), with Chinese and Indian ethnicities comprising 12% and 4% respectively. Common cardiovascular risk factors included dyslipidaemia (48%), diabetes mellitus (40%), hypertension (28%), a history of smoking (16%) and gout (8%). 20% of the patients had no other medical illness at the time of the index procedure. Culprit lesions were predominantly in the left anterior descending artery (LAD:72%), right coronary artery (RCA: 24%) and left circumflex artery (LCX:4%). Most patients presented with STEMI (64%), followed by NSTEMI (24%) and unstable angina (12%). For the LAD and RCA lesions, the bioadaptor sizes ranged from 2.5 to 3.5mm, with post dilatation up to 4.15mm. For the LCX lesion, a 2.5mm bioadaptor was used with post dilation up to 3.02mm. At 30 days and 18 months of follow up, 1 TLF event were reported: This event was a STEMI at 2 weeks post procedure attributed to clopidogrel resistance as intravascular ultrasound showed optimal scaffold expansion.



Conclusion
PCI with the DynamX bioadaptor scaffold in ACS patients was safe and shows promising short-term and intermediate-term outcomes, with 1 TLF event reported. Further investigation through larger prospective studies is needed to validate its long-term efficacy.


