Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-150
High Definition Intravascular Ultrasound Assessment in a Case of Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction With Calcified Coronary Arteries
By Debdatta Bhattacharyya, Saurabh Dhumale, Koushik Dasgupta
Presenter
Saurabh Dhumale
Authors
Debdatta Bhattacharyya1, Saurabh Dhumale2, Koushik Dasgupta3
Affiliation
RN Tagore Hospital, India1, Narayana Health Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, India2, NH-Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, India3,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-150
IMAGING AND PHYSIOLOGIC LESION ASSESSMENT - Imaging: Intravascular
High Definition Intravascular Ultrasound Assessment in a Case of Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction With Calcified Coronary Arteries
Debdatta Bhattacharyya1, Saurabh Dhumale2, Koushik Dasgupta3
RN Tagore Hospital, India1, Narayana Health Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, India2, NH-Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, India3,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
SM
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
59 year old diabetic, hypertensive gentleman presented with history of chest pain of >48 hours duration. Pain was variable in intensity over the period, radiating to left arm and jaw. He had erratic control of diabetes over past 4 years while he was on antihypertensives over the similar period with fairly controlled blood pressure. On examination, he was in sinus rhythm without signs of congestive heart failure.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
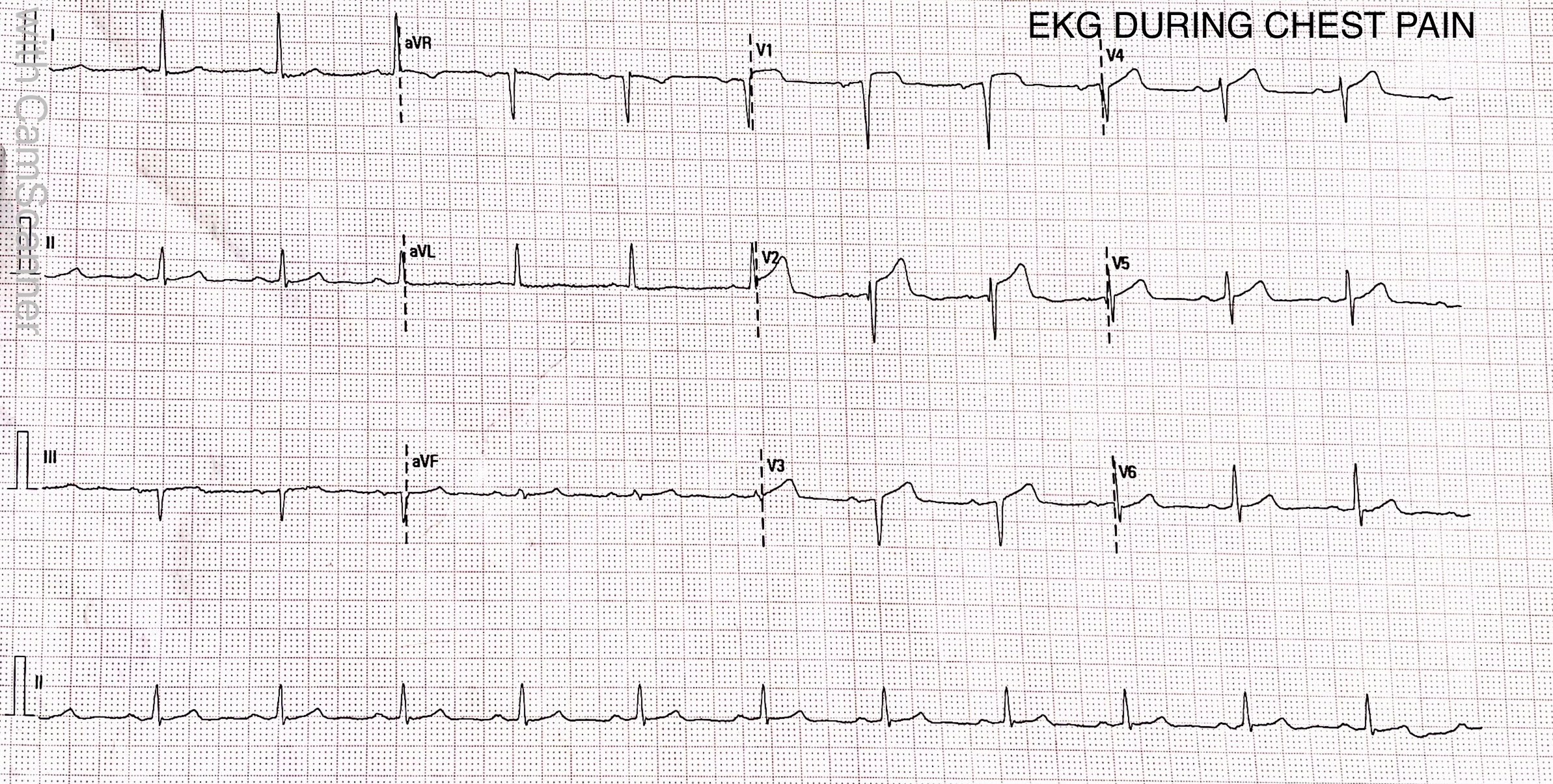
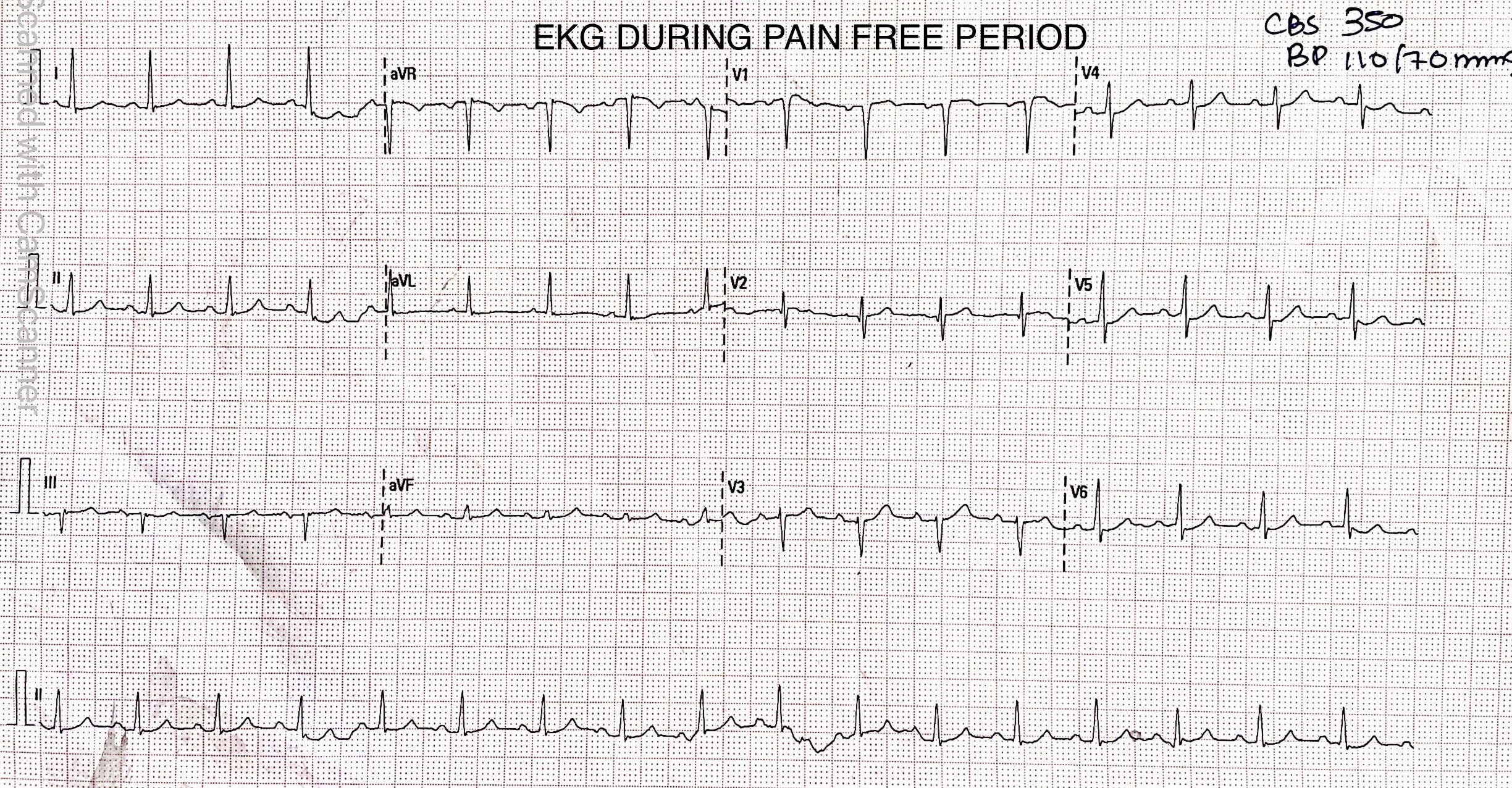
12 lead ECG showed sinus rhythm with 1-2mm ST segment elevationin V1,V2,V3 (dynamic ST segment changes with intermittent chest pain were observed over next 48 hours).Echocardiography showed hypo kinesis in the LAD territory with ejection fraction of 46%. His hemoglobin was 14.2 gm% , serum creatinine was 0.79 mg/dl,while highly sensitive troponin levels were elevated up to 13563 ng/L.


Relevant Catheterization Findings
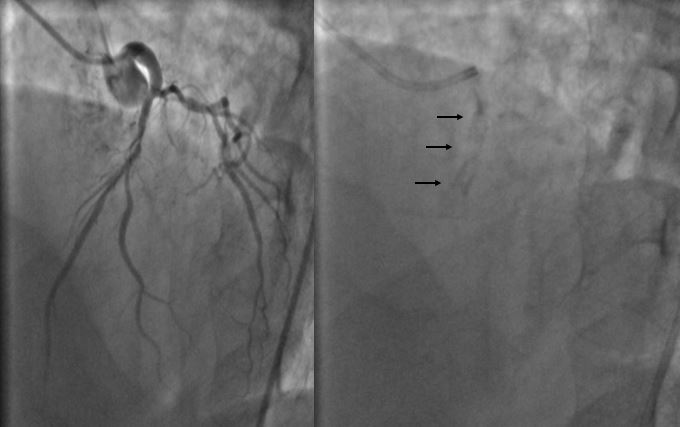
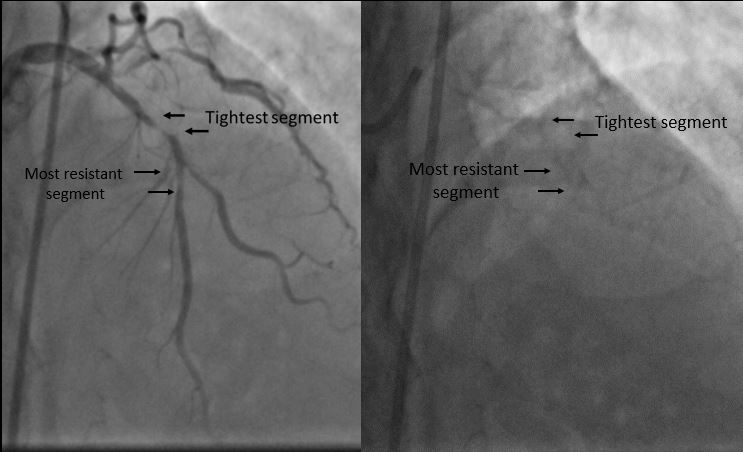
Mild tapering of distal left main coronary artery causing 30% stenosis was noted. The proximal left anterior descending artery showed long segment calcific disease with maximum of 90% stenosis prior to the second diagonal branch, while the segment distal to the second diagonal branch origin showed 50-60% stenosis. The Circumflex was non-dominant and free from significant disease while the right coronary artery was dominant with insignificant stenosis located at the distal postero-lateral branch.
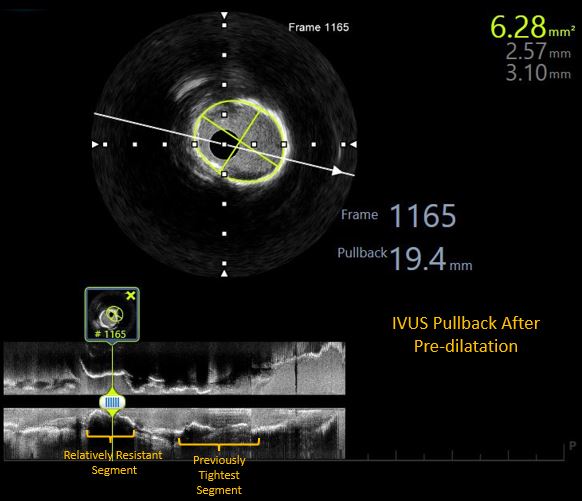



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Arterial access was obtained from right femoral artery. The left coronary artery was engaged with 7F XB 3.0 guide catheter. The lesion was crossed with a 0.014"X180 cm Run Through Intermediate wire. Thereafter, the artery was pre-dilated with 2.5X15mm non-compliant traveler balloon. Thereafter, a motorized IVUS pullback was performed with Atlantis Pro HD-IVUS catheter, which revealed a combination of superficial and deep calcium without any evidence of luminal thrombus or napkin ring type constricting sub-intimal stenosis. It helped us rule out the need for a calcium modification device and paved the way for further aggressive pre-dilatations. Based on this information, further pre-dilatations were carried out by 3.0X15mm & 3.5X15mm NC traveler balloons. Following this stenting was carried out from LAD ostium to mid-LAD with a 3.0X38mm DES. A fluoroscopic acquisition post stenting revealed an area of haziness at distal stent edge, which was confirmed to be an edge dissection with visible entry point by motorized IVUS pullback. Further stent implantation was done distally with a 2.75X23mm DES. Based on IVUS findings regarding luminal diameters, we did graded post-dilatations at high pressures with 3.0X15 NC balloon in mid-LAD and 3.5X15 NC balloon in proximal-LAD.
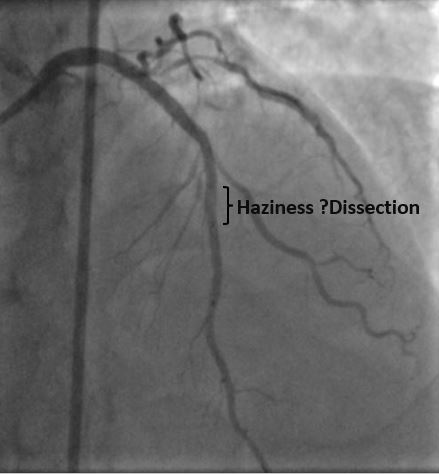
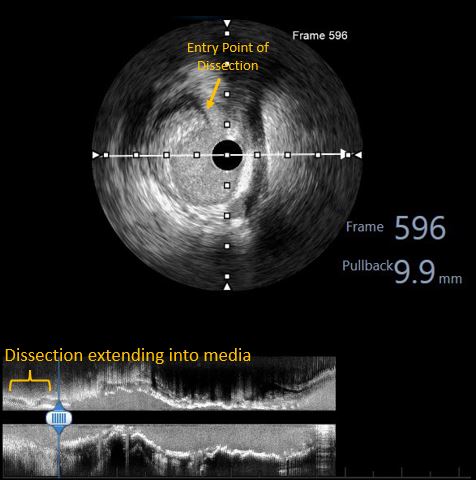
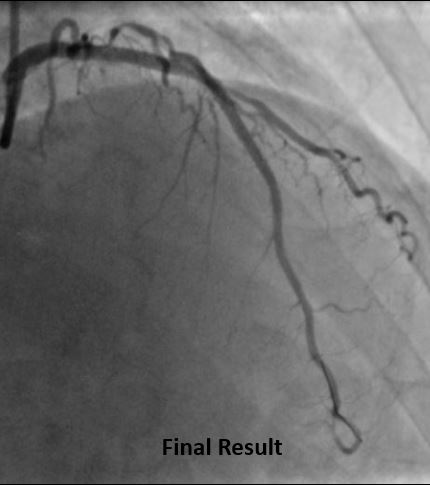



Case Summary
HD-IVUS offers better visualization of luminal and near-field vascular structures compared to conventional IVUS. In this case of NSTE-ACS with calcific coronary arteries, HD-IVUS was extremely helpful in excluding intraluminal thrombi and evaluating distribution of length and arc of calcium deposition and its relationship to the intima. This helped us in decision making regarding aggressive balloon dilatations prior to stenting. After pre-dilatation it confirmed adequate bed preparation with no further need for calcium modification therapies. Post stenting, it accurately picked up an edge dissection with great clarity, thus enabling us to complete the PCI successfully with further stenting.


