Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-112
Successful E-CPR and PCI in Case With Jailed Left Circumflex Artery With VT-Arrest After Left Main PCI
By Sirichai Wiriyatanakorn, Krissada Meemook
Presenter
Sirichai Wiriyatanakorn
Authors
Sirichai Wiriyatanakorn1, Krissada Meemook1
Affiliation
Ramathibodi Hospital, Thailand1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-112
CORONARY - Complications
Successful E-CPR and PCI in Case With Jailed Left Circumflex Artery With VT-Arrest After Left Main PCI
Sirichai Wiriyatanakorn1, Krissada Meemook1
Ramathibodi Hospital, Thailand1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
TB
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
TB was an 78 years old man with hypertension, dyslipidemia, and stage 3 chronic kidney disease. He had history of exertional angina for few months. Because of that, he went to hospital and his physician sent him to do an exercise-stress test. His EST was suggestive of myocardial ischemia. Then, he was scheduled for elective coronary angiography. His physical examination was unremarkable.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
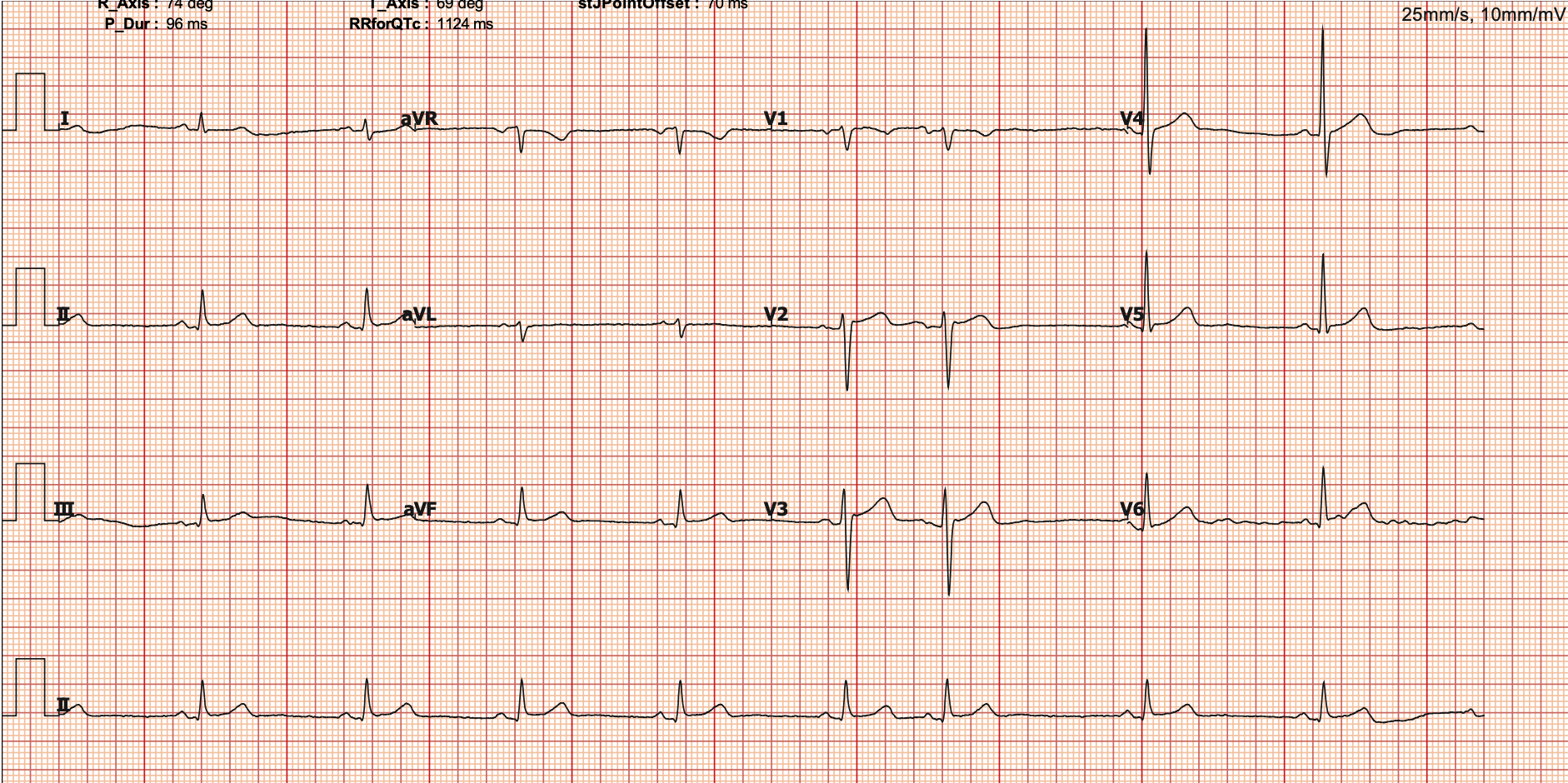
His resting electrocardiogram showed sinus bradycardia with rate of 55 bpm without significant ischemic change. During EST, his total exercise time was 5:30 minutes for standard BRUCE protocol and there was horizontal ST depression at lead II, III, aVF, V4, V5, and V6 at peak exercise.

Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiogram via right radial artery access using 5-Fr. Tiger catheter showed:
 CAG 04.mp4
CAG 04.mp4
 CAG 06.mp4
CAG 06.mp4
 CAG 07.mp4
CAG 07.mp4
- Left dominant system
- LM: heavily calcified with 70% stenosis at distal LM bifurcation
- LAD: diffuse severe stenosis from ostial to mid segment
- LCx: moderate stenosis at ostium, moderate stenosis at ostial 1st OM branch (small caliber) and 2nd OM branch
- RCA: non-dominant, long moderate stenosis at mid segment
The diagnosis was triple-vessel disease with LM. We planned to perform PCI of LM-LAD.
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
We engaged the LM artery using 6-Fr Guiding XB3.5 catheter. Sion Blue wire was at LAD and Runthrough guide was at LCx. IVUS at LM-LAD showed mixed calcium and fibrolipid plaque with severe stenosis from distal LM to mid LAD. We pre-dilated the lesion using 2.5-mm and 3.5-mm non-compliance (NC) balloons. Then, we put the Amphilimus-eluting stent size 3.50 x 46 mm to the LM-LAD. However, there was difficulty delivering the stent to the lesion because of heavy calcification and calcium nodule at distal LM. We used the GuidePlus extension catheter and switch guide wire from LCx to LAD for buddy-wire. After multiple attempts, we could finally position the stent and deployed at nominal pressure. Unfortunately, after stent deployment, the patient developed VT and VF. Angiogram showed completely jailed dominant LCx with TIMI-0 flow. CPR with defribillation and IABP insertion were performed immediately and we decided to initiate VA-ECMO. After completion of VA-ECMO cannulation and ROSC, we continued the PCI aiming to establish the flow at LCx. 4.0-mm NC balloon was used for POT of LM. Successful wiring of LCx was achieved by using Conquest Pro guide wire and Pilot200 guide wire with adjunct of Crusade dual-lumen microcatheter. Then, we changed to soft wire. 2.0-mm balloon was used to open the ostial LCx strut. Then, we stented the proximal LCx with 3.5 x 24 mm Everolimus-eluting stent. Then, we performed balloon kissing at LAD/LCx. POT of LM was done with 4.5-mm NC balloon.
 PCI 15 Post stent (Jailed LCx).mp4
PCI 15 Post stent (Jailed LCx).mp4
 PCI 41 Final angiogram.mp4
PCI 41 Final angiogram.mp4
 PCI 45 ECMO and IABP.mp4
PCI 45 ECMO and IABP.mp4
Case Summary
Learning points- Major side branch occlusion can be serious complication.- Bifurcation PCI using two-stent strategy should be considered in case of large/dominant side-branch.- Mechanical circulatory support is beneficial in high-risk PCI or in case of serious complication.


