Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-087
Revascularization in Patient With Left Main Coronary Artery Chronic Total Occlusion and Left Ventricular Dysfunction
By Cheng-Wei Lien, Hsien-Li Kao, Jiun-Yang Chiang
Presenter
Cheng-Wei Lien
Authors
Cheng-Wei Lien1, Hsien-Li Kao1, Jiun-Yang Chiang1
Affiliation
National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-087
CORONARY - Complex and Higher Risk Procedures for Indicated Patients (CHIP)
Revascularization in Patient With Left Main Coronary Artery Chronic Total Occlusion and Left Ventricular Dysfunction
Cheng-Wei Lien1, Hsien-Li Kao1, Jiun-Yang Chiang1
National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Chen
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
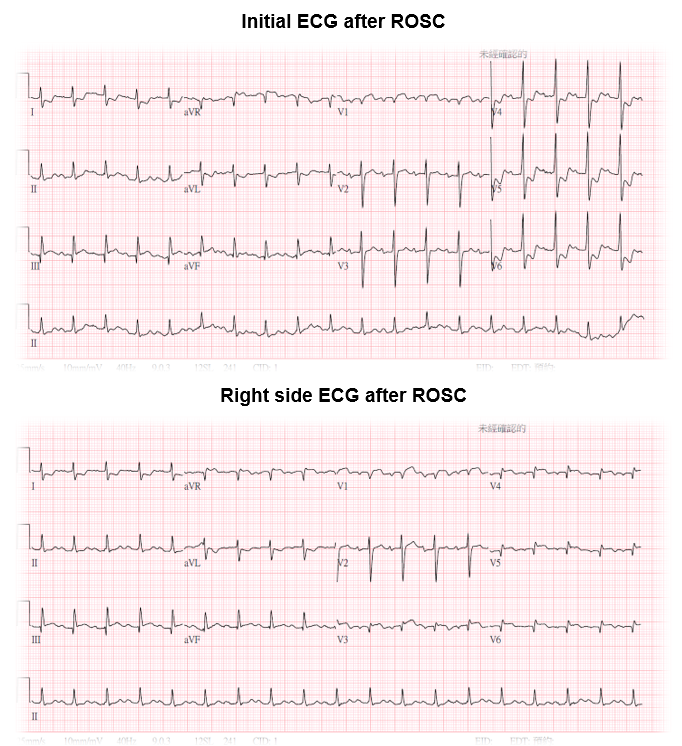
This 78-year-old man presented to our hospital due to OHCA. He had the past medical history of CAD and received bypass surgery 12 years ago. The initial ECG after ROSC showed inferior STEMI. Primary PCI was performed and RCA was revascularzied. However, after PCI, patient still suffered from lung edema and depended on NIPPV and inotropics. Intermittent angina was still noticed. The UCG showed severe LV dysfunction. Due to refractory heart failure, PCI was performed for total revascularization.
 1st PCI.mp4
1st PCI.mp4


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
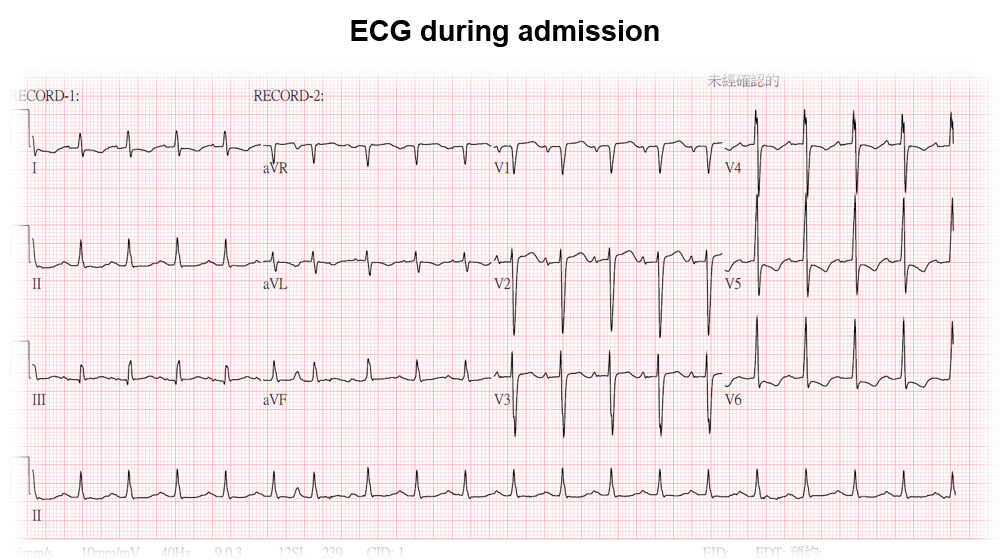
The ECG during admission showed persistent ST-depression at lead I, aVL and V4 to V6. The UCG showed severe LV dysfunction with ejection fraction 24.4 %.Biochemical study showed impaired renal function with serum creatinine 3.1 mg/dl and blood urea nitrogen 49.9 mg/dl.
 UCG A4C during admission.mp4
UCG A4C during admission.mp4

Relevant Catheterization Findings
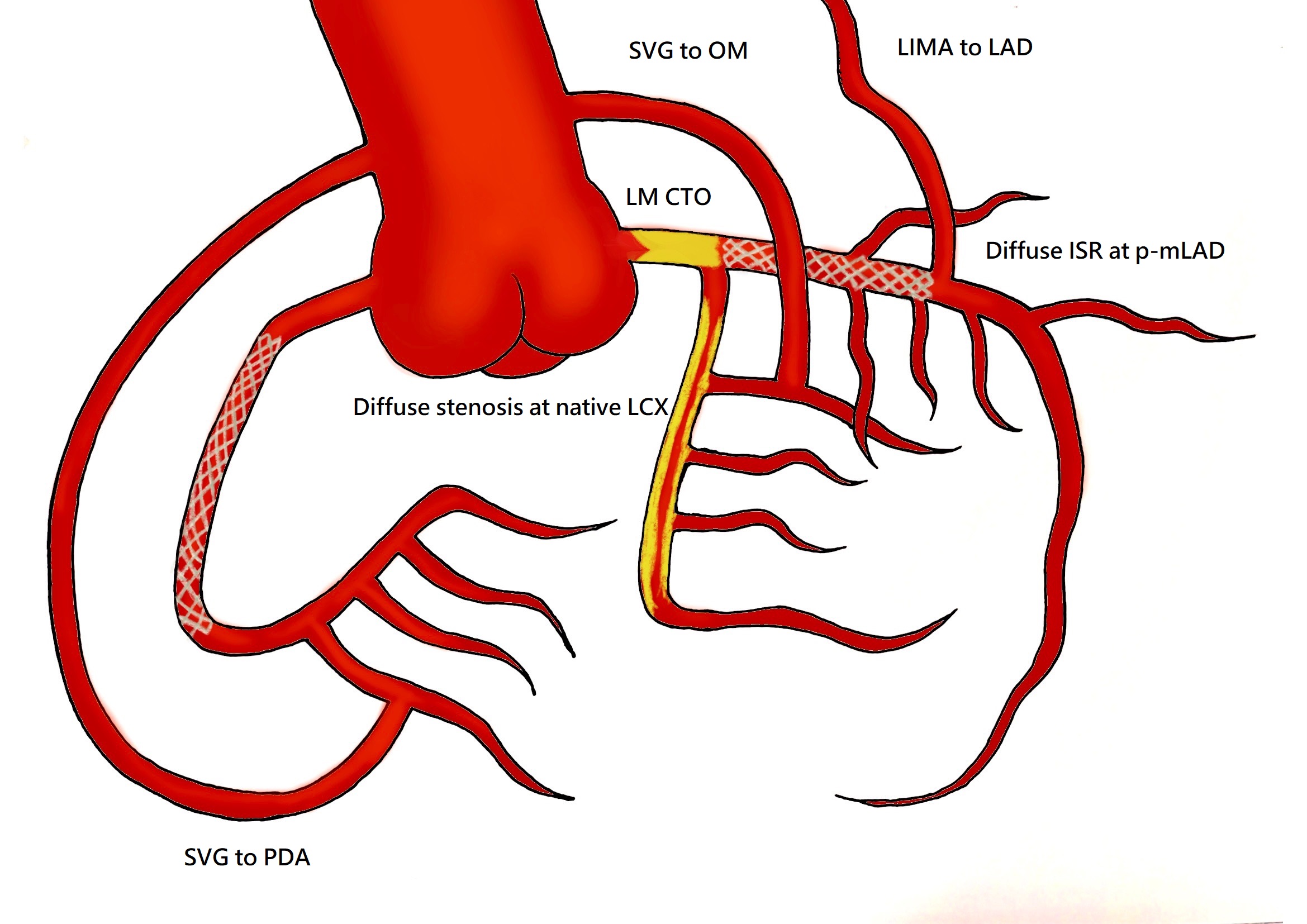
LM : total occlusion, with tapered tip, no calcification, absence of bending, occlusive length < 20 mm (J-CTO score 1)LIMA to LAD: patentNative LAD diffuse in-stent restenosisSVG to OM: patentNative LCX diffuse stenosisRCA: no in-stent restenosisSVG to PDA: patent
 CAG.mp4
CAG.mp4
 Dual injection.mp4
Dual injection.mp4

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
1. Elective endotracheal tube intubation was performed before the procedure. IABP was placed via right femoral artery due to high-risk coronary intervention.2. A Terumo 7 Fr. BL 3.5 was engaged to LM. 3. Tried to cross proximal cap of LM CTO with Sion black and Corsair support but failed.4. Successfully crossed LM CTO with GAIA Second and Corsair support.5. Balloon angioplasty was performed from LM to LAD with Ryurei PTCA balloon 1.5 x 10 mm and 2.0 x 15 mm.6. Checked IVUS from LM to LAD. IVUS showed underexpansion of previuos LAD stent and diffuse neointimal hyperplasia with calcified plaque.7. Rotational atherectomy was performed from LM to LAD with Rota Burr 2.0 mm up to 197000 rpm.8. The flow of LCX was compromised after rotational atherectomy from LM to LAD. 9. Successfully wired Sion Blue with Corsair support to distal LCX true lumen.10. Rotational atherectomy was performed to LCX with Rota Burr 2.0 mm up to 200000 rpm.11. Balloon angioplasty was performed at LAD with NSE ALPHA 2.5 x 13 mm and Accuforce 2.75 x 20 mm.12. Kissing balloon inflation was performed with NC Accuforce 2.75 x 20 mm at LAD and NC Accuforce 2.5 x 20 mm at LCX.13. Balloon angioplasty was performed at LAD with DCB SeQuent Please 2.75 x 40 mm and 3.0 x 30 mm.14. LM-LAD was stented with COMBO DES 3.5 x 23 mm.15. POT was performed at LM with NC Emerge 4.0 x 8 mm.15. The final angiography showed TIMI 3 flow at LAD. Due to prolong procedure time and contrast loading, the procedure was closed.
 Antegrade wiring success.mp4
Antegrade wiring success.mp4
 ROTA.mp4
ROTA.mp4
 Angioplasty and final.mp4
Angioplasty and final.mp4
Case Summary
1. IABP use can reduce procedural event rate and potentially reduce long-term mortality in appropriately selected patients who are at high risk of adverse events.2. The CTO lesions in post-CABG patients are more complex with increased calcification and anatomic ambiguity. 3. CTO crossing algorithms are useful tools for optimizing the success and safety of CTO PCI.


