Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-035
Coronary Lithotripsy for Underexpanded Stent and Orbital Atherectomy for Severely Calcified Native Coronary in NSTE-ACS
By Mohd Tawfeq Mohd Noor, Balachandran Kandasamy, Khai Chih Teh, Faten Aqilah Aris, Jassie Teo
Presenter
Mohd Tawfeq Mohd Noor
Authors
Mohd Tawfeq Mohd Noor1, Balachandran Kandasamy2, Khai Chih Teh1, Faten Aqilah Aris1, Jassie Teo1
Affiliation
National Heart Institute, Malaysia1, Subang Jaya Medical Centre, Malaysia2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-035
CORONARY - Adjunctive Procedures (Thrombectomy, Atherectomy, Special Balloons)
Coronary Lithotripsy for Underexpanded Stent and Orbital Atherectomy for Severely Calcified Native Coronary in NSTE-ACS
Mohd Tawfeq Mohd Noor1, Balachandran Kandasamy2, Khai Chih Teh1, Faten Aqilah Aris1, Jassie Teo1
National Heart Institute, Malaysia1, Subang Jaya Medical Centre, Malaysia2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Mr AA
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
70-year-old man with background history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidaemia and chronic kidney disease had percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to left anterior descending artery (LAD) 2 years ago. He was referred to our centre for non ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS). He presented with chest pain for 3 days prior to presentation. His blood pressure was 130/70 mmHg with heart rate 70 beat per minute.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Electrocardiogram showed T wave inversion in the anterior leads. Ejection fraction from echocardiography was 50%. Troponin T was elevated at 259 pg/ml (normal <14). His creatinine level was 170 umol/l (normal <100). The rest of blood parameters were unremarkable.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
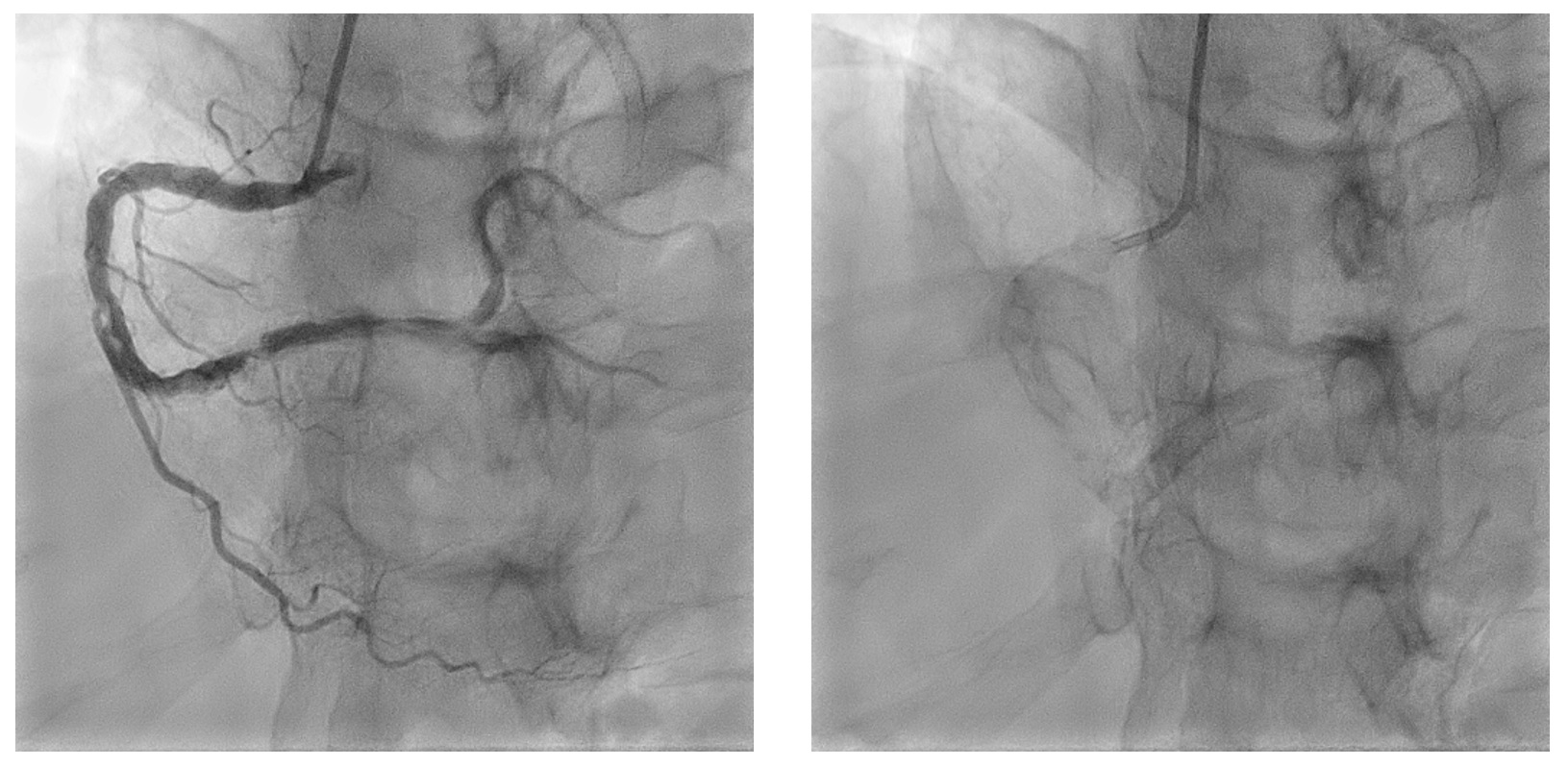
Coronary angiogram revealed mild left main artery (LM) disease. Left anterior descending artery (LAD) was heavily calcified with severe peri-stent stenosis, under expanded stent and in-stent restenosis (ISR). Left circumflex artery (LCX) had chronic total occlusion at ostial level while right coronary artery (RCA) showed severe calcified stenosis from mid to distal with calcium nodules.
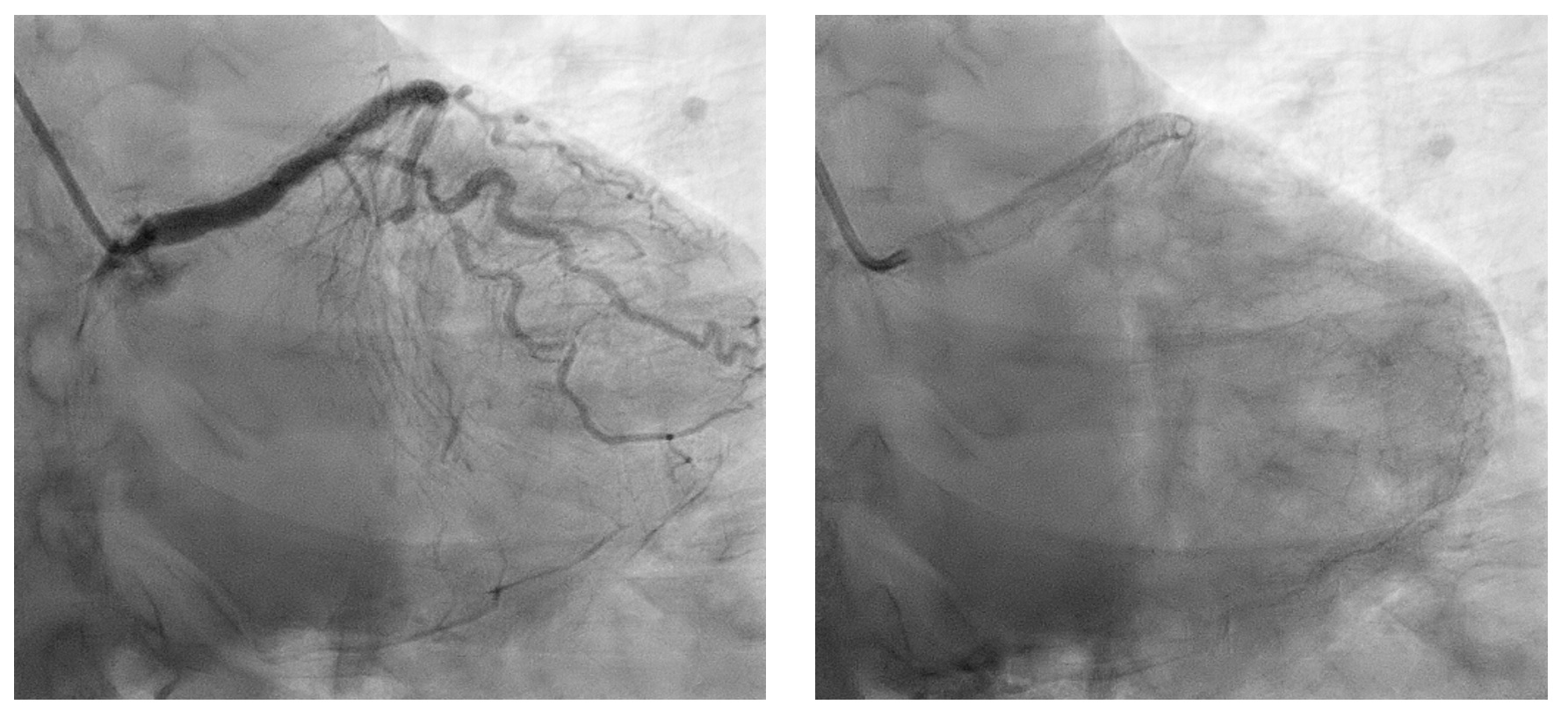
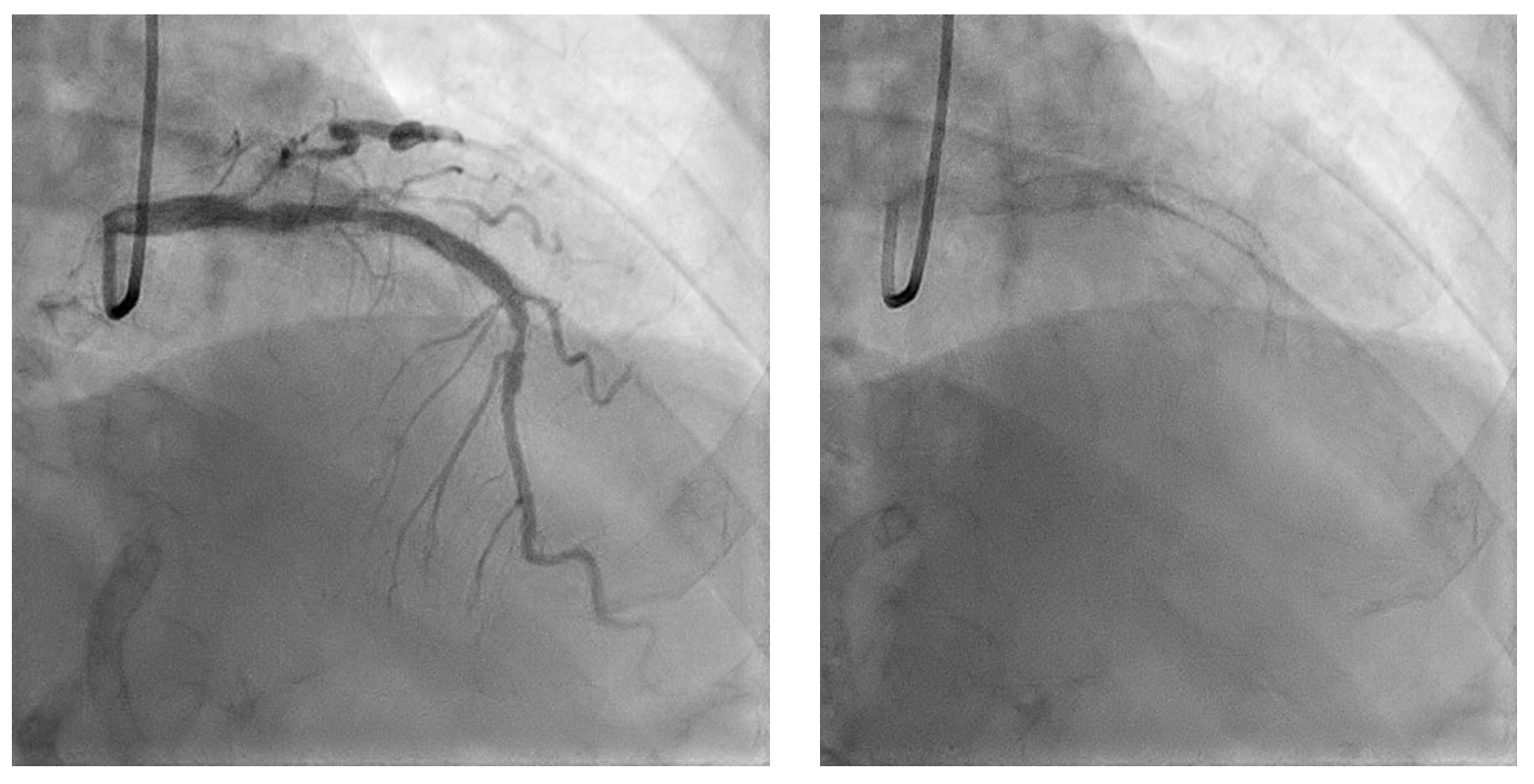



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
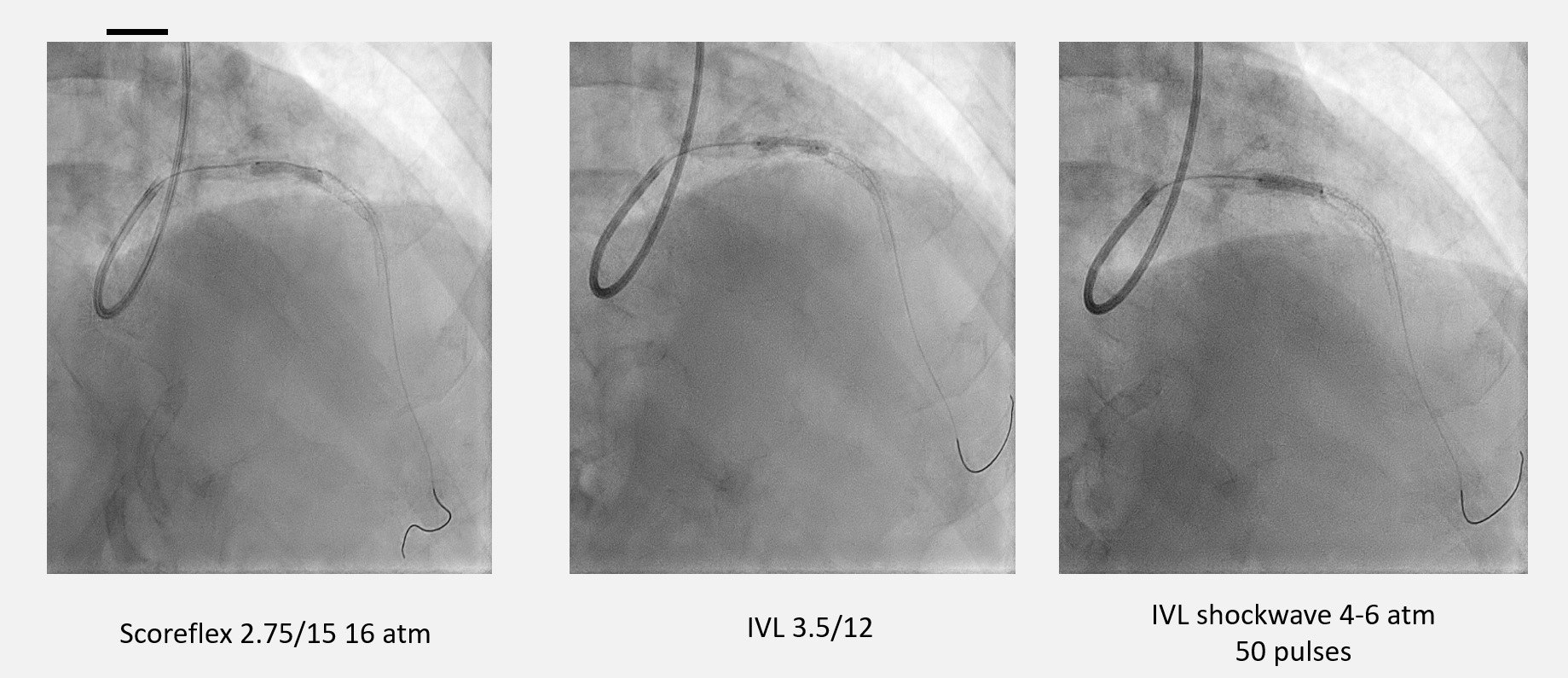
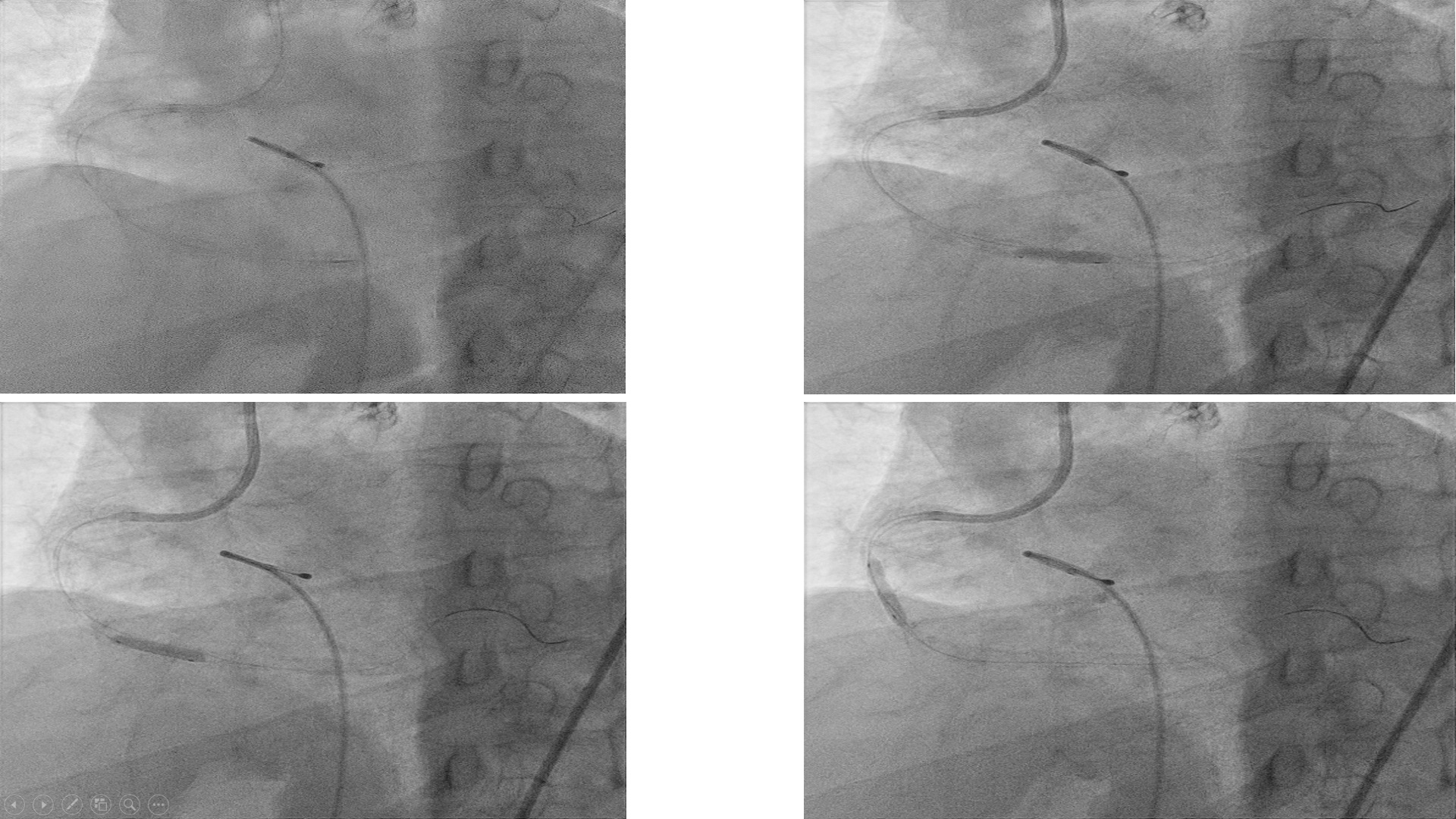
1. Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) LAD with Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) Pre-dilated distal ISR with Scoreflex 2.75 x 15 mm up to 16 atmosphere (atm) and proximal LAD, however lesions inadequately prepared. Decided to use IVL at proximal LAD 3.5 x 12 mm, shockwave at 4 - 6 atm for 50 pulses. Further prepared with non-compliant (NC) balloon 3.5 x 15 mm up 20 atm. Drug Coated Balloon (DCB) Sequent Please was then delivered to distal stent ISR : 2.75 x 20 mm. Stent Onyx 3.5 x 22 mm was deployed at proximal LAD, overlapped. Post-dilated with 4.0 x 12 mm NC Trek at 18 - 20 atm. IVUS showed well expanded and apposed stent. Mean Stent Area (MSA) 8.15mm2 at tightest point.
2. Orbital Atherectomy (OA) Right Coronary Artery with Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) OA to RCA was a staged procedure and was done 3 days after IVL to LAD.Temporary pacemaker was used as back up. OCT showed distal diameter 3.5 mm, calcium nodules, proximal reference 4.5 mm.
Micro catheter Teleport was used to exchange to Viper wireOA 80,000 - 120,000 rpm for 8 runs at the distal lesion, while 10 runs to the more proximal lesion. The lesions were optimized further with NC baloons.Stent Xience Sierra 3.5 x 33 mm deployed at distal, while at proximal Xience Sierra 4.0 x 33 mm. Post-dilated with NC Trek 4.0 x 15mm at 12 - 24 atm.
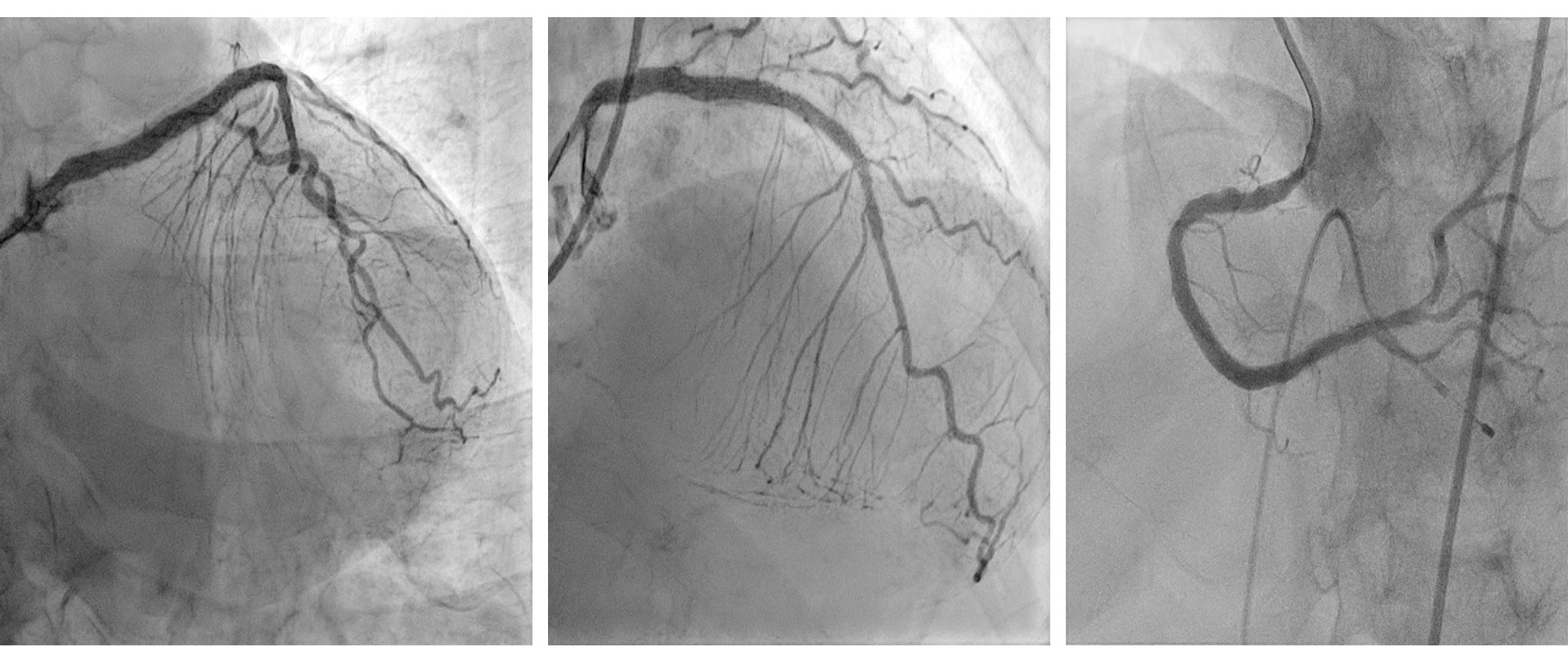
2. Orbital Atherectomy (OA) Right Coronary Artery with Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) OA to RCA was a staged procedure and was done 3 days after IVL to LAD.Temporary pacemaker was used as back up. OCT showed distal diameter 3.5 mm, calcium nodules, proximal reference 4.5 mm.
Micro catheter Teleport was used to exchange to Viper wireOA 80,000 - 120,000 rpm for 8 runs at the distal lesion, while 10 runs to the more proximal lesion. The lesions were optimized further with NC baloons.Stent Xience Sierra 3.5 x 33 mm deployed at distal, while at proximal Xience Sierra 4.0 x 33 mm. Post-dilated with NC Trek 4.0 x 15mm at 12 - 24 atm.



Case Summary
Coronary artery calcification complicates stent delivery and stent expansion. Stent under expansion is a strong predictor of restenosis and stent thrombosis, therefore appropriate plaque modification prior to stent implantation is essential in order to allow adequate device deployment. At present, there are limited options to treat refractory stent under expansion. In this case, the IVL system proven be a safe and effective strategy.


