Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-029
Impact of Residual SYNTAX Score on Clinical Outcomes After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention of Left Main Coronary Artery Disease
By Firman Noor Habibi, Udin Bahrudin, Ali Zaenal Abidin, Ardi Yudha, David Jonathan Pesireron, Devina Gabriella Nugroho, Susi Herminingsih, Ilham Uddin, Y Herry, Sodiqur Rifqi
Presenter
Firman Noor Habibi
Authors
Firman Noor Habibi1, Udin Bahrudin2, Ali Zaenal Abidin3, Ardi Yudha3, David Jonathan Pesireron3, Devina Gabriella Nugroho3, Susi Herminingsih3, Ilham Uddin3, Y Herry3, Sodiqur Rifqi3
Affiliation
Majalaya General Hospital, West Java, Indonesia, Indonesia1, Diponegoro University, Indonesia2, Dr. Kariadi General Hospital, Indonesia3
View Study Report
TCTAP A-029
Bifurcation/Left Main Diseases and Intervention
Impact of Residual SYNTAX Score on Clinical Outcomes After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention of Left Main Coronary Artery Disease
Firman Noor Habibi1, Udin Bahrudin2, Ali Zaenal Abidin3, Ardi Yudha3, David Jonathan Pesireron3, Devina Gabriella Nugroho3, Susi Herminingsih3, Ilham Uddin3, Y Herry3, Sodiqur Rifqi3
Majalaya General Hospital, West Java, Indonesia, Indonesia1, Diponegoro University, Indonesia2, Dr. Kariadi General Hospital, Indonesia3
Background
The majority of left main coronary artery diseases (LMCAD) are accompanied with multivessel disease which contributes to the incomplete revascularization in a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and its clinical outcomes. The residual SYNTAX score (rSS) is associated with clinical outcome post PCI, however, its prognostic value of rSS in LMCAD PCI remain unknown. Aim of this study was to investigate one-year clinical outcomes based on the residual SYNTAX score in patients with LMCAD underwent PCI.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study was conducted in patients with LMCAD underwent PCI at the Dr. Kariadi General Hospital from January 2017 to June 2021. The residual SYNTAX score was measured after a final PCI procedure, and then was classified as rSS ≤ 8 and rSS > 8. The clinical outcomes were major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (MACCE) and all-cause mortality. The MACCE was defined as composite of all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction, stroke and repeat revascularization. Statistical analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier curve and multivariate cox regression.
Results
A total of 215 from 270 subjects was enrolled in this study. In-hospital mortality rate was 0.9 % and one-year mortality was 3.3 %. The numbers of patients with rSS ≤ 8 and > 8 were 169 and 46, respectively. There was no difference in all-cause mortality events within two groups (2.3% vs. 6.5%; HR 2.8, 95% CI 0.64–12.85; p= 0.14). However, patients with rSS > 8 had a higher rate of MACCE (4.7 % vs. 30.4%; HR 7.5, 95% CI 3.18–18.09; p< 0.0001).
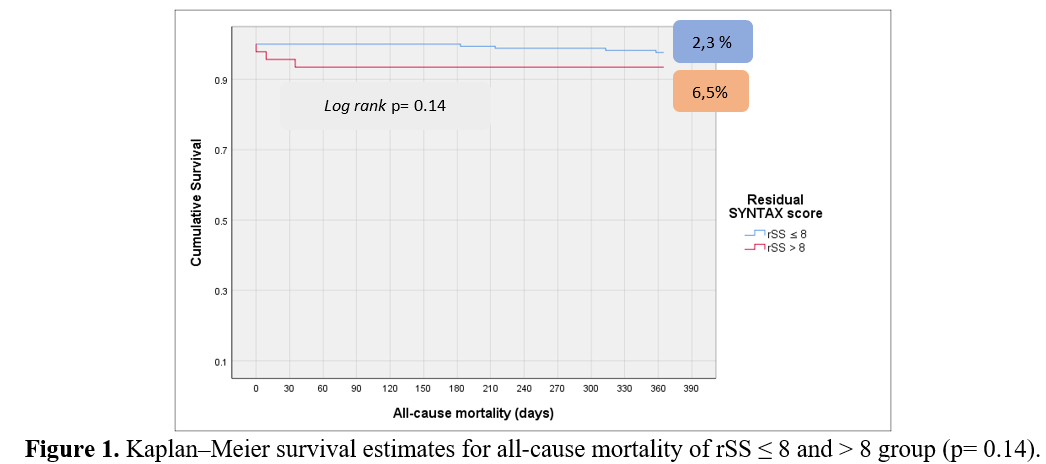
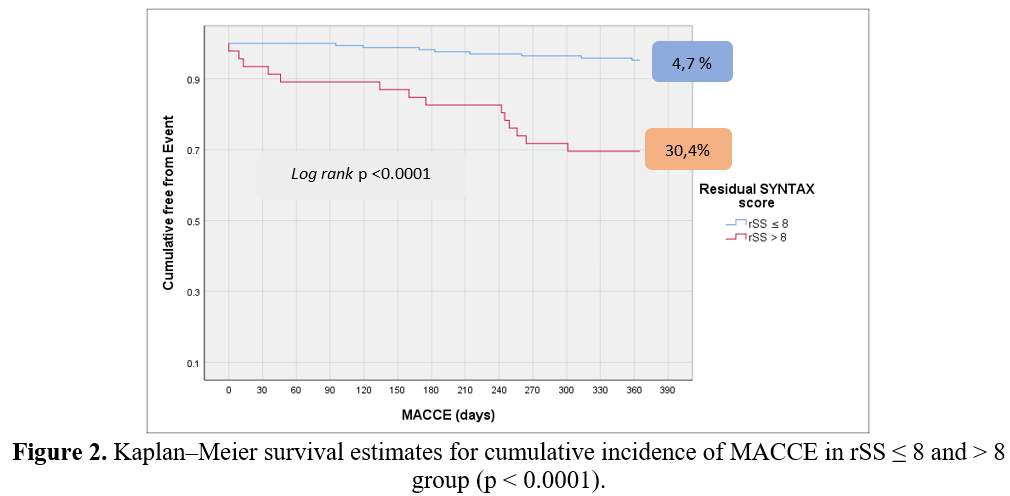


Conclusion
In patients with LMCAD underwent PCI, residual SYNTAX score > 8 is associated with higher one-year MACCE, but not all-cause mortality, than that of the residual SYNTAX score ≤ 8.


