Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-025
The Impact of Renal Function on the Clinical Outcomes of Rotational Atherectomy.
By Korakoth Towashiraporn, Rungroj Krittayaphong, Damras Tresukosol, Rewat Phankingthongkum, Wiwun Tungsubutra, Nattawut Wongpraparut, Narathip Chunhamaneewat, Asa Phichaphop, Pariya Panchavinnin, Treenet Reanthong, Chunhakasem Chotinaiwattarakul
Presenter
Korakoth Towashiraporn
Authors
Korakoth Towashiraporn1, Rungroj Krittayaphong, Damras Tresukosol, Rewat Phankingthongkum, Wiwun Tungsubutra, Nattawut Wongpraparut, Narathip Chunhamaneewat, Asa Phichaphop, Pariya Panchavinnin, Treenet Reanthong, Chunhakasem Chotinaiwattarakul
Affiliation
Her Majesty Cardiac Center Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand1
View Study Report
TCTAP A-025
Adjunctive Procedures (Thrombectomy, Atherectomy, Special Balloons)
The Impact of Renal Function on the Clinical Outcomes of Rotational Atherectomy.
Korakoth Towashiraporn1, Rungroj Krittayaphong, Damras Tresukosol, Rewat Phankingthongkum, Wiwun Tungsubutra, Nattawut Wongpraparut, Narathip Chunhamaneewat, Asa Phichaphop, Pariya Panchavinnin, Treenet Reanthong, Chunhakasem Chotinaiwattarakul
Her Majesty Cardiac Center Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand1
Background
Coronary calcification, which is typically observed in chronic kidney disease patients, is related to subsequent adverse cardiovascular events. Calcified coronary artery causes percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to be more challenging, as calcified plaque results in the suboptimal immediate outcomes of PCI such as stent mal-apposition or stent underexpansion. Therefore, leading to future stent-related complications such as in-stent restenosis or stent thrombosis. Rotational atherectomy (RA) uses a dedicated diamond-coated burr to debulk the calcified plaque. As a result, RA-assisted PCI improves immediate and long-term clinical endpoints.
Methods
This single-center study was conducted at Her Majesty Cardiac Center Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. We enrolled 528 patients who underwent RA-assisted PCI and whose creatinine levels were accessible between January 2015 and December 2018. This study aims to identify the risk factors for developing major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (MACCE) at 1-year follow-up by using cox’s proportional hazards regression model. MACCE consists of cardiac death, ischemic stroke, definite stent thrombosis, target lesion revascularization, and target vessel revascularization. We used the restricted cubic spine graphs to demonstrate the relationship between serum creatinine and MACCE.
Results
The mean age was 72.6 ± 9.7 years. 53.8% were female. The incidence of 1-year MACCE was 7.39%. The mean serum creatinine was significantly higher in the MACCE group (2.8 ±2.7 mg/dl [MACCE] versus 1.8 ± 2.0 mg/dl [no-MACCE]; p = 0.048). The use of intravascular imaging was significantly higher in the no-MACCE group(51.3% [MACCE] versus 75.3% [no-MACCE]; p = 0.006). Using multivariate analysis, increased in serum creatinine (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 1.16, 95%confidence interval [95% CI] (1.04 – 1.30); p = 0.010), female gender (adjusted HR 1.9, 95% CI (1.00 – 3.63); p = 0.0049) and the history of coronary artery bypass graft (adjusted HR 2.53, 95% CI (1.11 – 5.73); p = 0.027) were independent risk factors for developing MACCE (Figure 1). Figure 2 demonstrates the relationship between serum creatinine and MACCE. The cut point of serum creatinine that contributed to the escalation of the MACCE rate was 1.4 mg/dl.
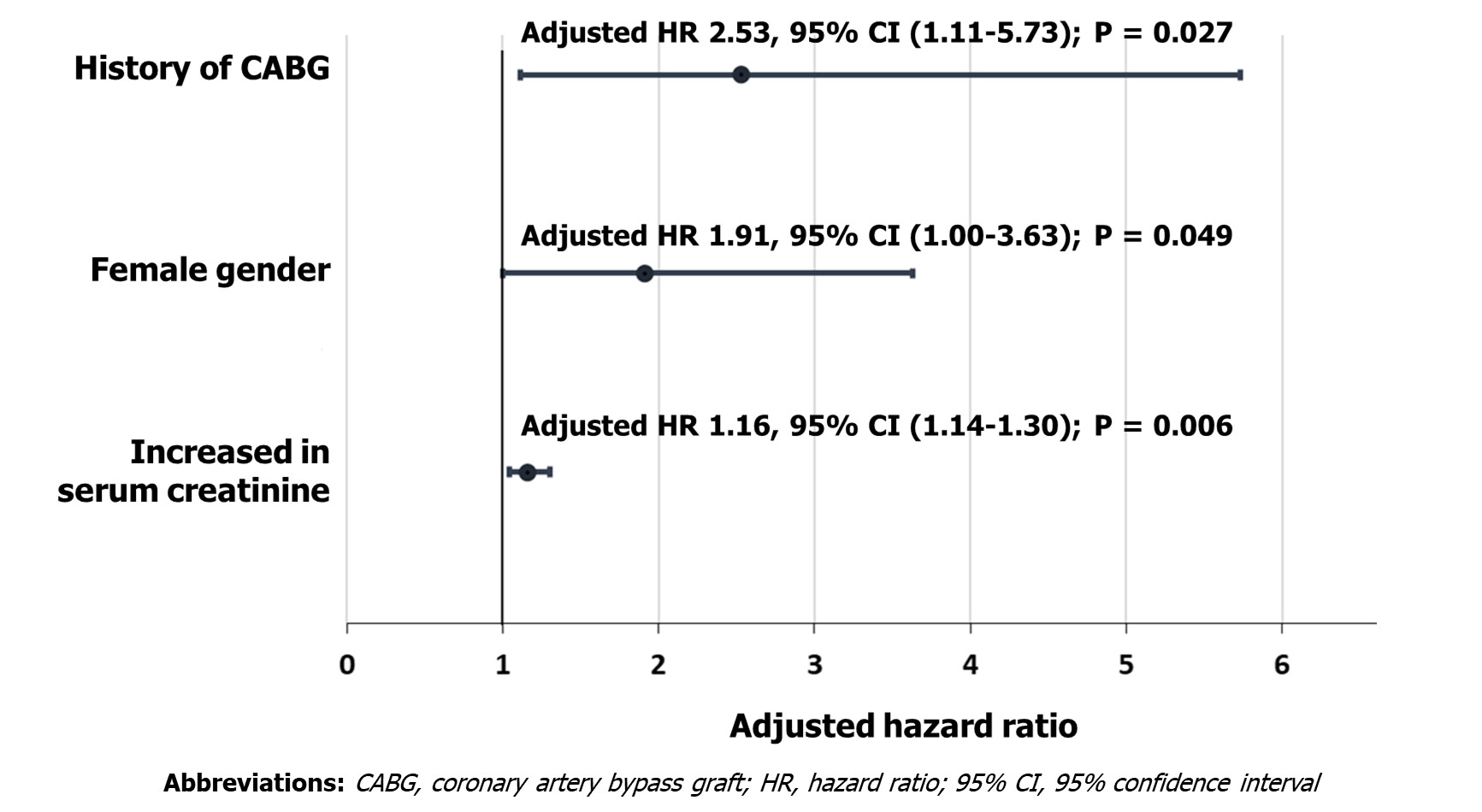
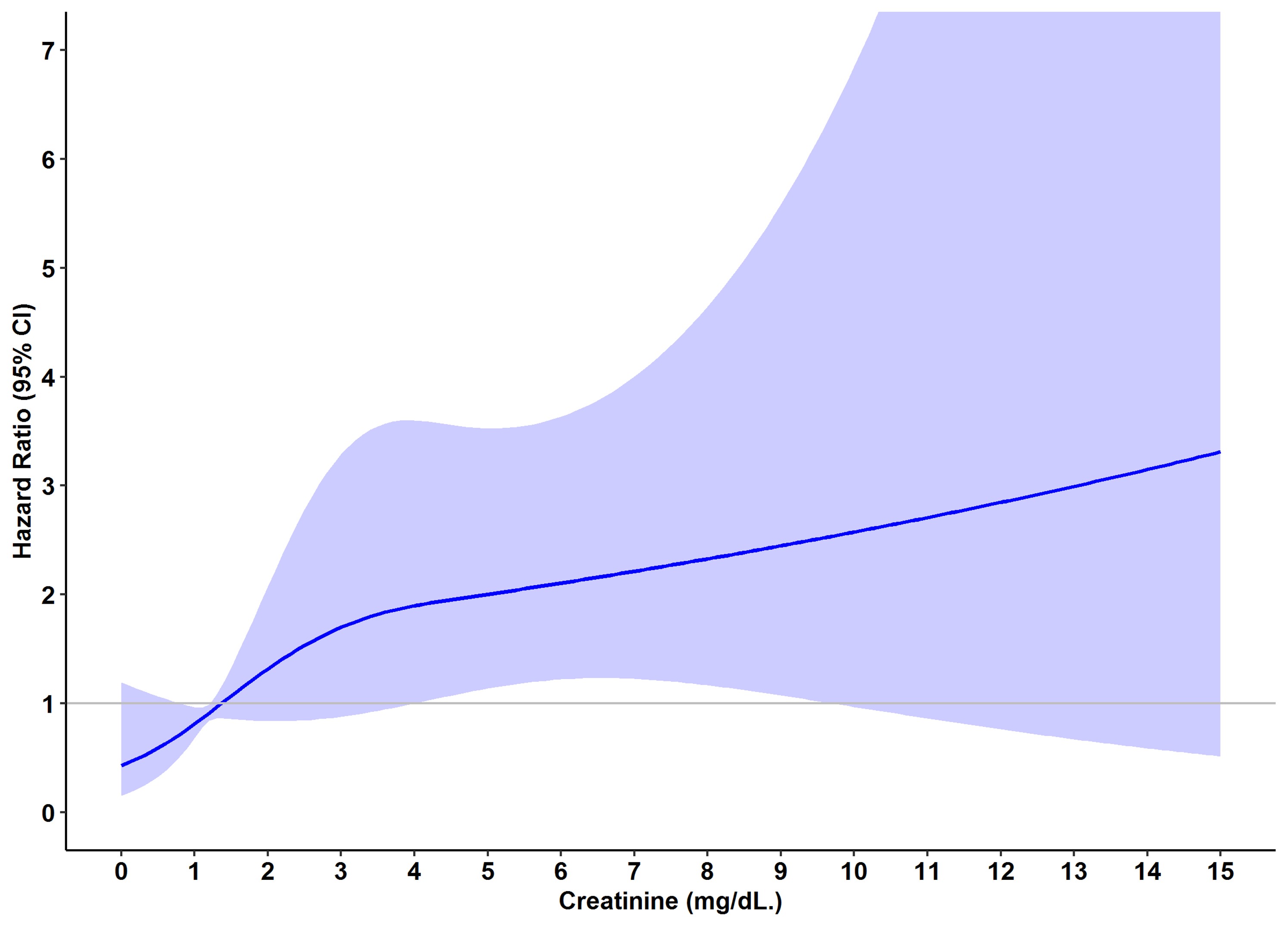


Conclusion
Rotational atherectomy is feasible for treating calcified coronary artery lesions as this procedure provides good long-term clinical follow-up. This present study demonstrates the relationship between renal function and the clinical outcomes of RA-assisted PCI—the higher the serum creatinine level, the greater risk of developing MACCE.


