Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2021 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
TCTAP C-018
Presenter
Siddhartha Mani
Authors
Debdatta Bhattacharyya1, Siddhartha Mani2, Ayan Kar2
Affiliation
RN Tagore Hospital, India1, NH-Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, India2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-018
CORONARY - Adjunctive Procedures (Thrombectomy, Atherectomy, Special Balloons)
Complex Calcific Anomalous Right Coronary Artery PCI with Rotablation
Debdatta Bhattacharyya1, Siddhartha Mani2, Ayan Kar2
RN Tagore Hospital, India1, NH-Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, India2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
MRK
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
68-year female non diabetic, normotensive.Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarction one month back conservatively managed.Now presents with post infarct angina and shortness of breath.Clinically frail and elderly.
 MRK first CAG.avi
MRK first CAG.avi
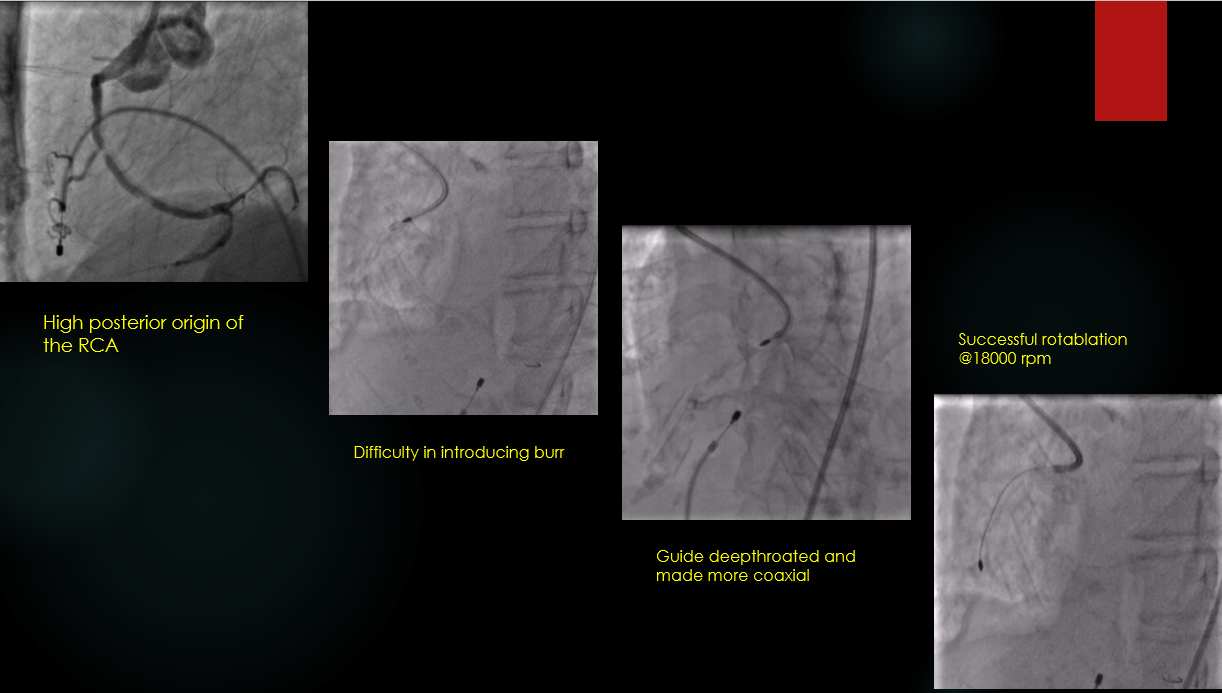
 difficulty in passing rotaburr.avi
difficulty in passing rotaburr.avi

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Hemoglobin 10.8g/dlcreatinine: 0.89 g/dl12 lead ECG :q in II,III,aVFEcho: hypokinetic infero-postero-lateral wall with an LVEF of 40%, presence of mitral annular calcification



Relevant Catheterization Findings
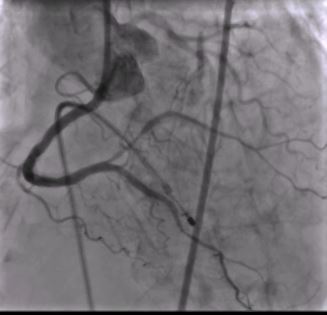
LMCA: normalLAD: large caliber vessel with tram track calcium and no 40-50% diseaseLCX: non dominant and free from significant diseaseRCA: anomalous high posterior origin, dominant vessel, long segment calcific disease involving the proximal mid and distal RCA with a tight 90 % lesion in the mid RCA
 MRK final result.avi
MRK final result.avi
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
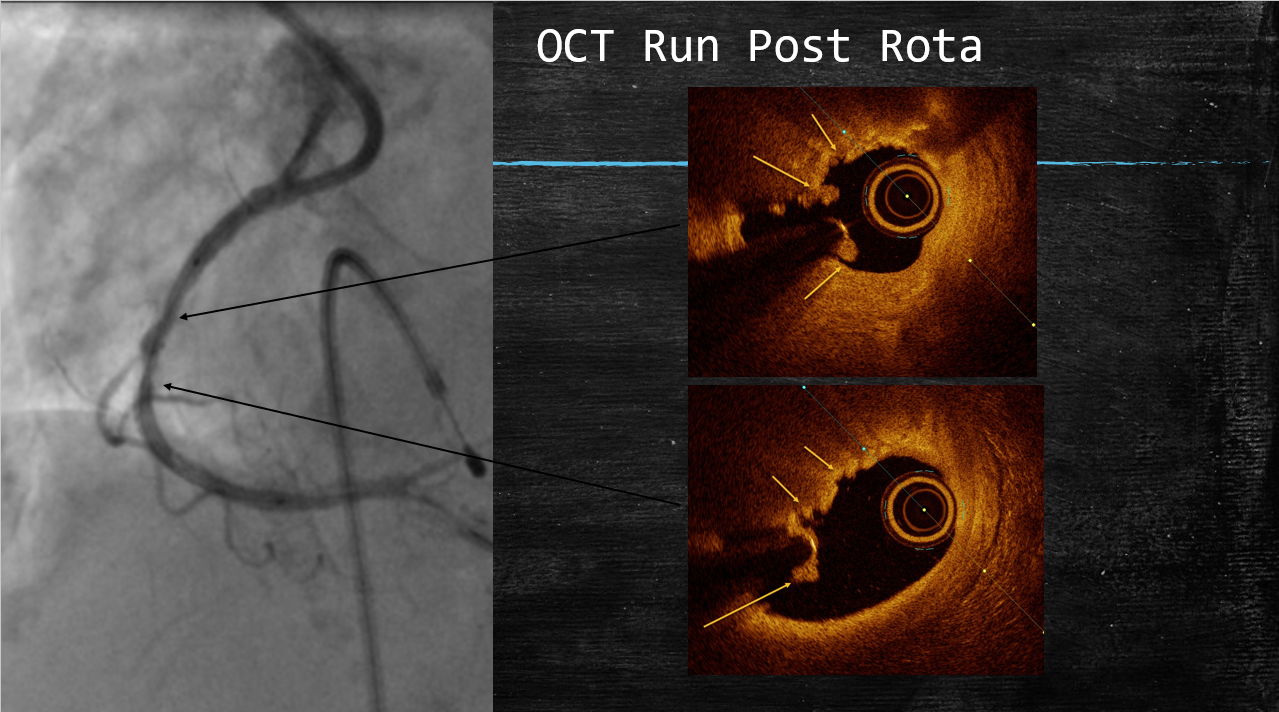
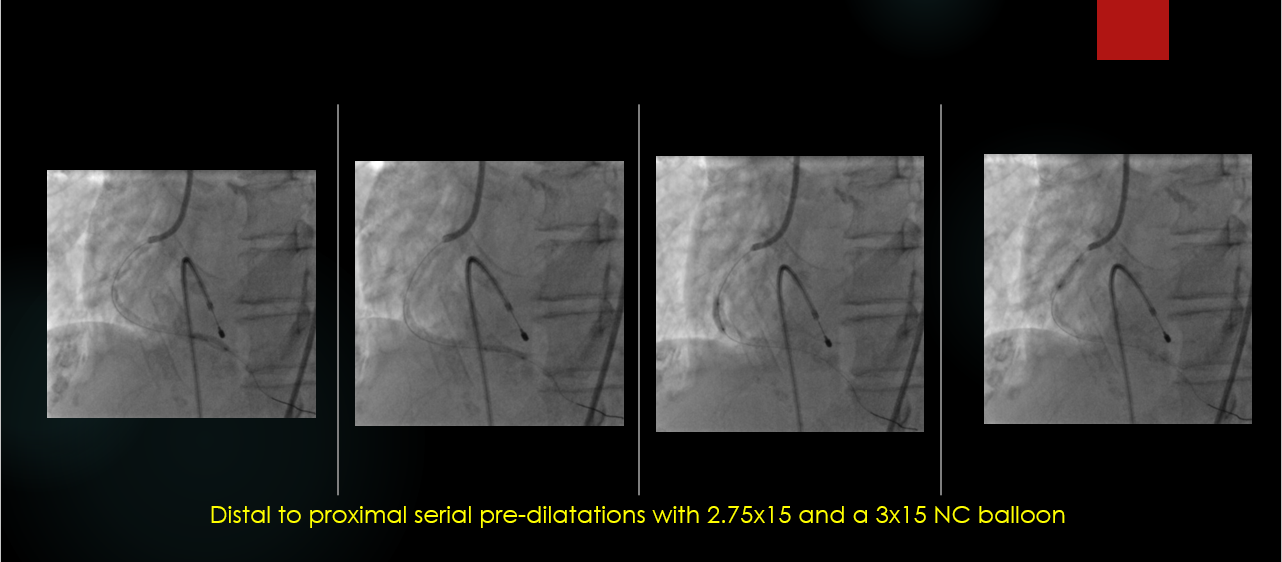
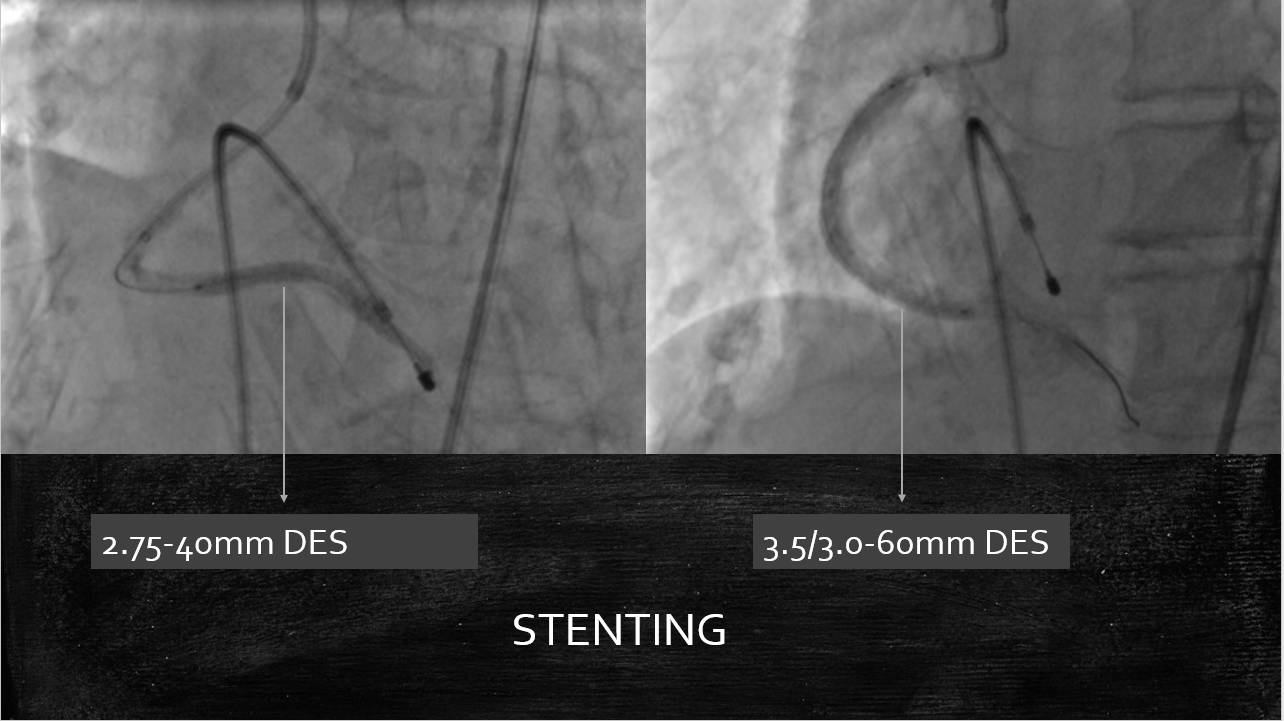
The RCA was engaged with 7Fr JR 3.5 GC.The RCA was wired with standard work-horse wire which was exchanged to rota-floppy wire over a microcatheter.Initial Rota burr advancement was difficult due to non coaxial alignment due to anomalous high posterior origin of RCA. The catheter was hence deep throated into the RCA over a 2.0x15mm balloon and checked for co-axiality in 3 diff views. Then Rotablation was done with a 1.5 mm burr at 1,80,000 rpm. There was transient slow flow and CHB which was treated with coronary vasodilators and temporary pacing. After the polishing run, OCT was performed to the RCA for vessel sizing, plaque and calcium assessment. It showed cuts in the sub-intimal calcification with controlled dissections.Following this, serial graded pre-dilatations were done to the RCA with 2.75x15 and 3x15 NC balloon at 16-24 ATM. Subsequently, two DES 2.75x 40mm and a 3,5-3.0x60 mm DES were implanted at nominal pressures and thoroughly postdilated.
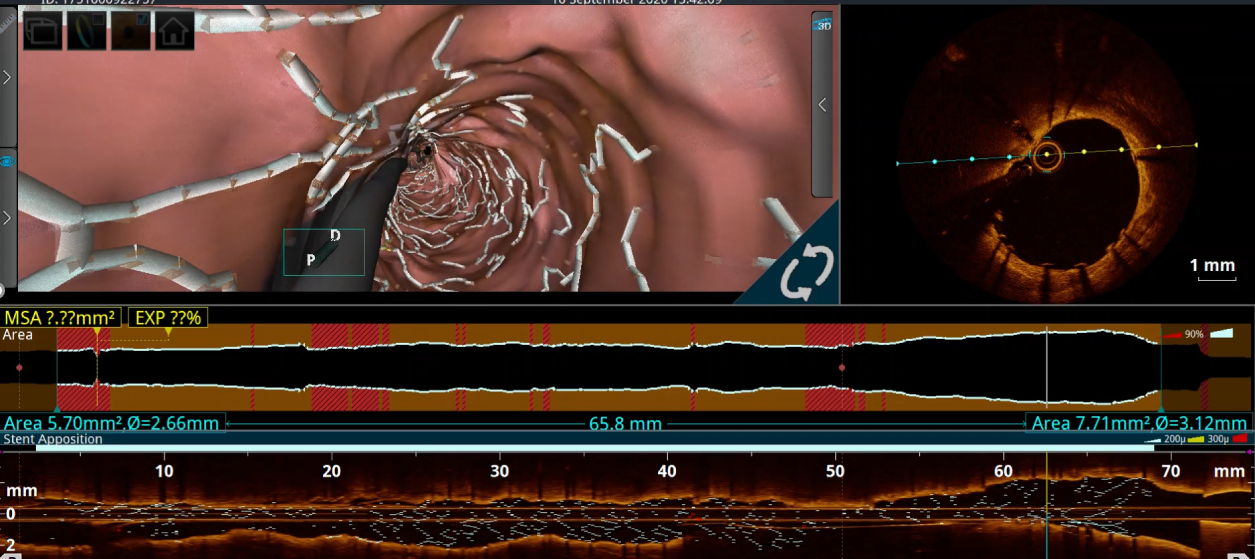
 final 3d flythough RCA.mp4
final 3d flythough RCA.mp4


Case Summary
▪During Rotablation of RCA, care should be taken regarding proper burr orientation with respect to vessel lumen before commencement of burring.
▪Long segment calcific disease is more likely to cause slow flow and its attendant complications.
▪Intravascular imaging after the rota-run is helpful in forming stenting strategies and requirement for further plaque modification.
▪Due care should be taken regarding post-rota vessel optimization with further balloon dilatation before implanting stents.
▪Stenting should be followed by careful post-dilatation with final intravascular imaging to confirm adequate stent deployment.


