Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2021 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
TCTAP A-041
Presenter
Donna Shu-Han Lin
Authors
Donna Shu-Han Lin1, Jen-Kuang Lee2
Affiliation
Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, Taiwan1, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan2
View Study Report
TCTAP A-041
Peripheral Vascular Disease and Intervention
Interwoven Self-expanding Nitinol Stent with Drug-coated Balloon Angioplasty for the Treatment of Severely Calcified Superficial Femoral Artery Lesions: Two-year Outcomes
Donna Shu-Han Lin1, Jen-Kuang Lee2
Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, Taiwan1, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan2
Background
Drug-coated balloon (DCB) angioplasty has limitations for the treatment of severely calcified femoropopliteal artery (FPA) lesions, due to inconsistent drug delivery, and the risk of dissections, vascular recoil and late lumen loss. Angioplasty with DCB followed by stenting with an interwoven, self-expanding nitinol stent, SUPERA might be a plausible approach to address these limitations and improve clinical outcomes.The objectives of this study are: (1) to compare the effectiveness and safety of DCB + SUPERA with DCB alone in treating severely calcified superficial femoral artery (SFA) lesions; and (2) to analyze the clinical outcomes based on the severity of vascular calcification.
Methods
This is a single-center, retrospective study. Data was collected from the medical records of all patients with severely calcified SFA lesions who underwent endovascular therapy with SUPERA + DCB or DCB only from August 2017 to June 2018. The primary endpoint was freedom from clinically driven-target lesion revascularization (CD-TLR) at 24 months. Secondary outcomes included freedom from CD-TLR at 24 months based on the severity of calcification and treatment strategy and rates of amputation and mortality.

Results
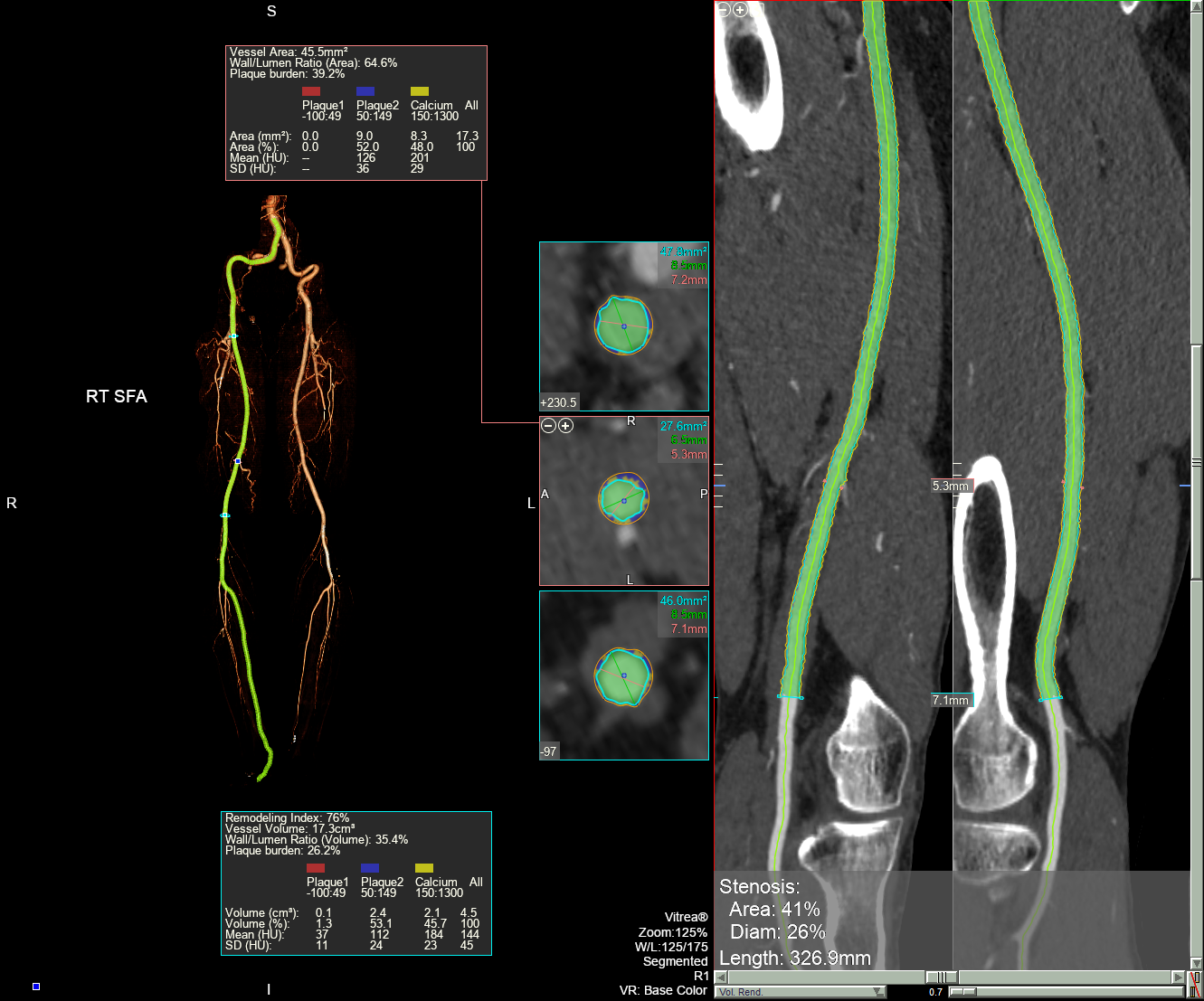
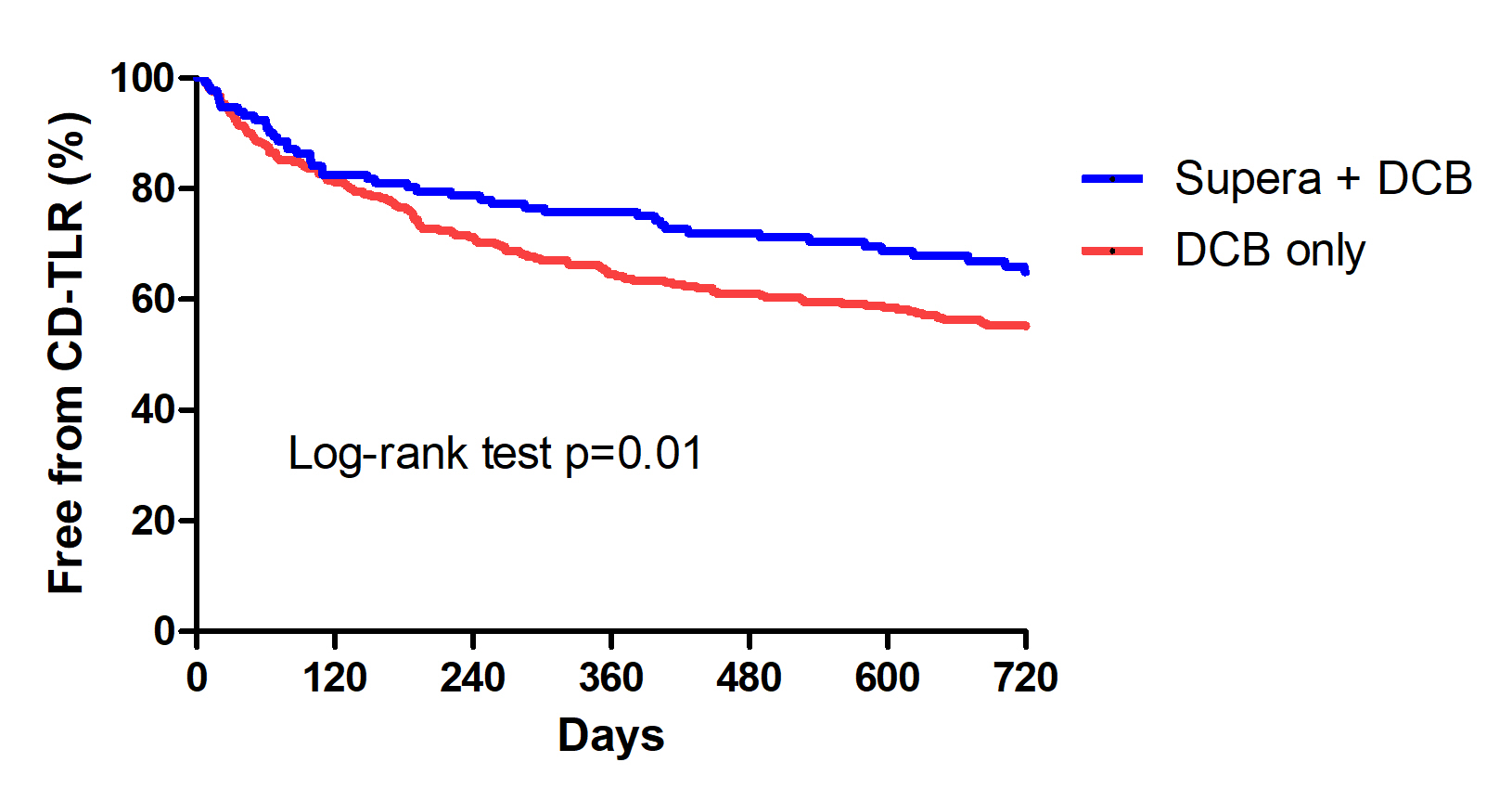
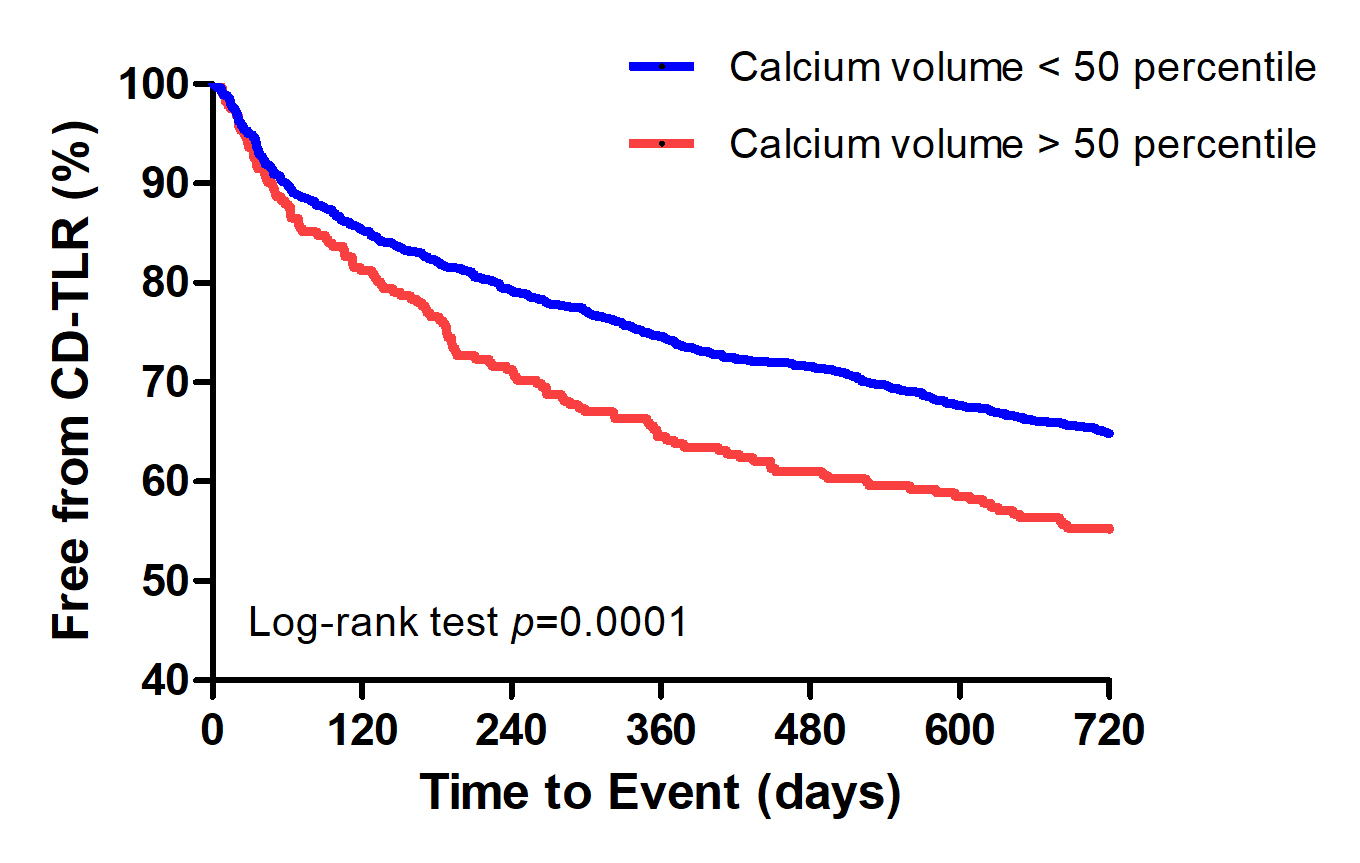
A total of 124 and 263 patients were treated with SUPERA+ DCB and DCB alone, respectively during the study period. About 76.9% of patients in the DCB + SUPERA arm and 80.4% in the DCB alone arm had diabetes; 41.2% and 45.6% had dialysis-dependent renal failure; and 35.2 % and 34.3% belonged to Rutherford category V. TASC D lesions were present in 35.2% and 33.1% of the patients, respectively. Freedom from CD-TLR at 24 months was significantly high in the DCB + SUPERA versus DCB alone group (66.3% versus 54.9%; p=0.01). The favorable freedom from CD-TLR rates with DCB + SUPERA was noted regardless of the severity of vascular calcification. Patients with calcium volume below versus above the 50th percentile had significantly better freedom from CD-TLR rates at 24 months. Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that pre-operative non-ambulatory status, dialysis-dependent renal failure, TASC D FPA lesions, calcium volume above 50th percentile and insulin treatment were significant predictors of CD-TLR. While, advanced age, pre-operative non-ambulatory status, dialysis-dependent renal failure, and calcium volume above the 50th percentile were significant predictors of amputation. Interwoven stent implantation was associated with lower rates of CD-TLR and amputations on both univariate and multivariate analyses.


Conclusion
Angioplasty with DCB followed by SUPERA implantation showed superior results in terms of freedom from CD-TLR at 24 months for the treatment of severely calcified SFA lesions compared to DCB angioplasty alone. Vascular calcification severity had a negative impact on the outcomes.


